A validated HPTLC method for quantification of active compounds in a Polyherbal formulation Guggulutiktam Kashayam
*Article not assigned to an issue yet
C T Sulaiman, Raihana Thasreef, T Shafna, R Ramesh P, K Mahesh, M Praveen, E M Anandan, Balachandran Indira
Research Articles | Published: 11 February, 2025
First Page: 0
Last Page: 0
Views: 2009
Keywords: Guggulutiktam Kashayam, HPTLC, Polyherbal formulation, Caffeic acid, Scopoletin
Abstract
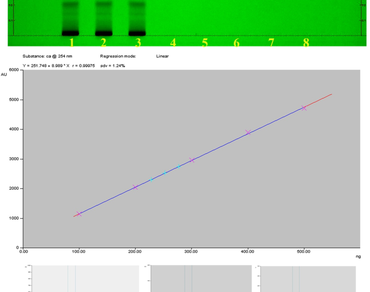
Guggulutiktam Kashayam (GTK) is an important Polyherbal formulation used in Ayurveda for the treatment of various ailments such as ulcers, cardiac diseases, skin disorders, arthritis and cancer. It is prepared from parts of 29 plants. Polyherbal formulations are rich in active phytochemicals. Active phytochemicals like Caffeic acid and Scopoletin have been quantified in GTK by a validated HPTLC method. Analysis was carried out using CAMAG HPTLC system equipped with auto sampler, documentation unit and densitometry scanner. The method was validated in terms of assessing precision, accuracy, linearity, specificity, robustness, limit of detection (LOD) and limit of quantification (LOQ) as per the International Council for Harmonization (ICH) Guidelines. The quantity of Caffeic acid and Scopoletin in GTK are found to be 0.0262 (%w/w) and 0.00209 (%w/w) respectively. A novel and validated HPTLC method has been developed for the quantification of active compounds of an important Ayurvedic formulation which can be used as a powerful analytical tool for the quality standardization of the formulation. This method can also be used for the quality checking of similar types of other Polyherbal formulations.
References
Antika LD, Tasfiyati AN, Hikmat H, Septama AW (2022) Scopoletin: a review of its source, biosynthesis, methods of extraction, and pharmacological activities. Z Naturforsch C 77:303–316
Bouyahya A, Guaouguaou FE, El Omari N, El Menyiy N, Balahbib A, El-Shazly M, Bakri Y (2022) Anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties of Moroccan medicinal plants: Phytochemistry, in vitro and in vivo investigations, mechanism insights, clinical evidences and perspectives. J Pharm Anal 12:35–57
Çakır DK, Zannou O, Koca I (2022) Scopoletin contents and antioxidant properties of some edible plants of Black Sea regions. Discover Food 2
Choudhary N, Sekhon BS (2011) An overview of advances in the standardization of herbal drugs. J Pharm Educ Res 2(2):55–70
Espíndola KMM, Ferreira RG, Narvaez LEM, Silva Rosario ACR, da Silva AH, Silva AGB, Vieira APO, Monteiro MC (2019) Chemical and Pharmacological aspects of Caffeic Acid and its activity in Hepatocarcinoma. Front Oncol 21
Gao XY, Li XY, Zhang CY, Bai CY (2024) Scopoletin: a review of its pharmacology, pharmacokinetics, and toxicity. Front Pharmacol 15
Hornick A, Lieb A, Vo NP, Rollinger JM, Stuppner H, Prast H (2011) The coumarin scopoletin potentiates acetylcholine release from synaptosomes, amplifies hippocampal long-term potentiation and ameliorates anticholinergic- and age-impaired memory. Neuroscience 197(1):280–292
ICH Harmonised- Tripartite Guideline (2023) Nov
Khunluck T, Kukongviriyapan V, Senggunprai L, Duangarsong W, Prawan A (2019) The inhibition kinetics and potential anti-migration activity of NQO1 inhibitory coumarins on cholangiocarcinoma cells. Integr Cancer Ther 18
Patel U, Girme A, Patel K, Ghule C, Hingorani L, Gandhi T (2021) A validated HPTLC method for quantification of cordifolioside A, 20-β-hydroxyecdysone and columbin with HPTLC–ESI–MS/MS characterization in stems of Tinospora cordifolia. J Planar Chromatogr 34:217–228
Pavlíková N (2022) Caffeic acid and diseases-mechanisms of action. Int J Mol Sci 24:588
Rollinger JM, Hornick A, Langer T, Stuppner H, Prast H (2004) Acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activity of scopolin and scopoletin discovered by virtual screening of natural products. J Med Chem 47(25):6248–6254
Sahu U, Chauhan NS, Parihar AKS, Karbhal KS, Inchulkar SR, Gupta PK, Singh RK (2024) Development of simultaneous HPTLC method and validation for the Quality Assessment of Ayurvedic Formulation-Ayush Kvatha Churna by using marker compound Rosmarinic Acid, Trans-Cinnamaldehyde and Piperine. J Chromatogr Sci
Sharma A, Dhal C, Srivastava R (2019) A comparative estimation of the morphine content of the ayurvedic formulation ‘KaminiVidrawanRas’ using validated high-performance thin-layer chromatography and high-performance liquid chromatography techniques. J Planar Chromatogr 32(1):47–50
Silva T, Oliveira C, Borges F (2014) Caffeic acid derivatives, analogs and applications: a patent review (2009–2013). Expert Opin Ther Pat 24:1257–1270
Sona D, Baghel GS, Chandravanshi L, Sahu S, Chauhan NS, Kumar A, Gupta PK (2022) High-performance thin-layer chromatography-based quantification of therapeutic phytochemicals in the methanolic extract of ayurvedic formulation Drakshavaleha. J Planar Chromatogr 35:117–125
Spagnol CM, Assis RP, Brunetti IL, Isaac VLB, Salgado HRN, Corrêa MA (2019) In vitro methods to determine the antioxidant activity of caffeic acid. Spectrochim Acta A 219:358–366
Starek M, Homa K, Stępińska J, Dąbrowska M (2023) Development of thin-layer chromatography–densitometry for the quantification of lecithin in dietary supplements. J Planar Chromatogr 36:99–110
Sulaiman CT, Ramesh PR, Mahesh K, Madhu KM, Anandan EM, Praveen M, Balachandran I (2020) Chemical profiling of a polyherbal formulation by tandem mass spectroscopic analysis with multiple ionization techniques. Future J Pharm Sci 6:40
Sulaiman CT, Shafna T, Advaya GR, Ramesh PR, Mahesh K, Praveen M, Anandan EM, Balachandran I (2023) Comparative chemical profiling of a polyherbal formulation with respect to its ingredient plants using spectrophotometric and high-performance thin-layer chromatographic techniques. Pharmacogn Mag 19:917–925
Author Information
Phytochemistry Division, Centre for Medicinal Plants Research, Arya Vaidya Sala, Kottakkal, India