Assessment of the incidence and severity of foliar fungal diseases in black aromatic rice
*Article not assigned to an issue yet
Thangjam Bijeeta, Devi Ph Sobita, Sinha Bireswar, Chakrapani Kota, Chanu W Tampakleima, SardaDevi K, Devi Y Premika, Chakma Tusi, Singh LNK, Devi Th Renuka
Research Articles | Published: 06 August, 2025
First Page: 0
Last Page: 0
Views: 94
Keywords: Aromatic rice, Blast, Brown spot, Sheath blight, Disease incidence and severity
Abstract
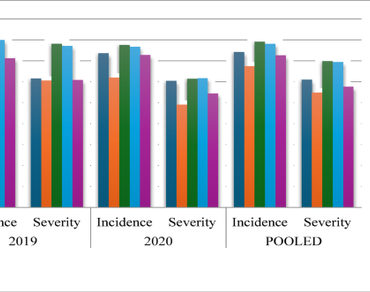
A survey was conducted on aromatic rice during the kharif seasons of 2019 and 2020 in the five valley districts of Kakching, Thoubal, Bishnupur, Imphal-East, and Imphal-West, Manipur to assess the natural disease occurrence of blast, brown spot and sheath blight diseases. The survey revealed that disease incidence and severity varied with locations. Blast, brown spot, and sheath blight have an overall disease incidence of 36.94%, 37.15%, and 37.34%, respectively, and severity of 34.62%, 31.28%, and 36.92%, respectively. Of the five valleys surveyed, Imphal East recorded the maximum mean incidence (41.80%) and severity (39.61%) of blast and Bishnupur recorded the maximum mean incidence (39.53%) and severity (34.90%) of brown spot disease. However, sheath blight incidence was higher in Imphal East valley (39.0%) and its severity was higher in Bishnupur (39.61%). The current research could pave the way for future management measures against the specific disease and an efficient, coordinated approach to the sustainable development of crops in the state.
References
Abrol S, Ahanger SA, Basu U, Mehta A, Singh SK, Singh VB, Vaid A (2022) Distribution pattern and prevalence of brown spot of rice (Bipolaris oryzae) in Jammu region. Pharma Innov 11(2):732–736
Chahal SS, Ratan GS, Sokhi SS (2003) Investigations on sheath blight of rice in Punjab. Indian J Pl Pathol 56:22–26
Chakrabarti NK (2001) Epidemiology and disease management of brown spot of rice in India. Major fungal diseases of rice. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 293–306
Chethana BS, Deepak CA, Rajanna MP, Ramachandra C, Shivakumar N (2016) Current scenario of rice diseases in Karnataka. Int J Nat Sc 7(2):405–412
Dar SM, Hussain S, Nabi GH, Majaz M (2010) Prevalence and distribution of blast disease (Magnaporthe grisea) on different components, of rice plants in paddy growing areas of the Kashmir Valley. Int J Pharm Bio Sci 1(3):1–4
Gangopdhyay S, Chakrabarti NK (1982) Sheath blight of rice. Ann Rev Pl Pathol 61:451–460
Gashaw G, Alemu T, Tesfaye K (2014) Morphological, physiological and biochemical studies on pyricularia Grisea isolates causing blast disease on finger millet in Ethiopia. J Appl Bio Sci 74:6059–6071
Hossain M, Ali MA, Hossain MD (2017) Occurrence of blast disease in rice in Bangladesh. Am J Agric Sci 4(4):74–80
IRRI (2013) Standard evaluation system for rice, 5th edn. International Rice Research Institute (IRRI), Manila, Philippines
Lavanya B, Gnanamanickam SS (2000) Molecular tools for characterization of rice blast pathogen (Magnaporthe grisea) population and molecular marker assisted breeding for disease resistance. Curr Sci 78(3):248–257
Manandhar HK (2017) Rice diseases and management in Nepal. Rice Science and Technology in Nepal-A Historical, Socio-cultural and Technical Compendium, 454–474
Margani R, Hadiwiyono, Widadi S (2018) Utilizing Bacillus to inhibit the growth and infection by sheath blight pathogen, Rhizoctonia solani in rice. In IOP conference series: Earth Environ Sci (Vol. 142, p. 012070). IOP Publishing
Mew TW, Gonzales P (2002) A Handbook of Rice seed borne fungi. Las Banos, Laguna, Philippines. pp 83 https://doi.org/10.22004/ag.econ.281818
Meya AI, Mamiro DP, Kusolwa P (2015) Response of late blight disease resistant-variety to common occurring tomato diseases in the field. Asian J Plant Sci 5(6):8–15
Mia MAT, Holderness M, Pearce D, Rahman M (2001) Effect of seed-borne bipolaris oryzae on seed germination and disease development in the field. Bangladesh J Pl Pathol 17(1–2):59–62
Naveenkumar R, Anandan A, Singh V, Prabhukarthikeyan SR, Parameswaran C, Sangeetha G, Ali J (2022) Deciphering environmental factors and defense response of rice genotypes against sheath blight disease. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 122:101916
Ou H 2 (2021) Rice Diseases 2nd edn.(Commonwealth Mycological Institute, Kew, 1985). Sci Rep, 11, 4786
Rajarajeswari NVL, Muralidharan K (2006) Assessments of farm yield and district production loss from bacterial leaf blight epidemics in rice. Crop Prot 25(3):244–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cropro.2005.04.013
Rao KM (1995) Sheath blight disease of rice. Daya Publishing House, Delhi, p 146
Singh NI (1987) Incidence of rice panicle stalk blast in Manipur. Internat Rice Res News 12(4):34–35. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.7123185
Singh RP, Shukla P, Singh PN (1979) Note on assessment of losses in rice due to brown leaf spot diseases. Indian J Agric Res 13:57–58
Singh VP (2000) The basmati rice of India. In: Singh RK, Singh US, Khush GS (eds) Aromatic rices. Indian Oxford & IBH Publishing Co Pvt Ltd, New Delhi, pp 136–153
Sunder S, Singh RAM, Agarwal R (2014) Brown spot of rice: an overview. Indian Phytopathol 67(3):201–215
Webster RK, Gunnell PS (eds) (1992) Compendium of rice diseases (pp. viii+-62)
Wheeler BEJ (1969) An Introduction to Plant Diseases. The English language Book Society And Wiley and Sons Ltd. pp.145–150
Yaduman R, Lal AA, Singh S (2018) Survey and occurrence of sheath blight disease (Rhizoctonia Solani Kuhn) of rice (Oryza sative L.) in rice growing areas of Allahabad. India J Pharmacog Phytochem 7(1):2239–2241
Yashaswini C, Madhav MS, Pushpavati B (2017) Morphological and molecular variability among rice blast pathogen (Magnaporthe oryzae) isolates in Southern. India Environ Eco 35(4B):3015–3022
Author Information
Department of Plant Pathology, College of Agriculture, CAU, Imphal, India