Comparative structural and techno-functional properties of barnyard, browntop and little millet starch by dielectric gas discharge and vacuum plasma
*Article not assigned to an issue yet
Srivastava Yashi, Chandwani Nisha, Dave Purvi Kikani, Patil Chirayu
Research Articles | Published: 30 May, 2025
First Page: 0
Last Page: 0
Views: 800
Keywords: Barnyard, Browntop, Little Millet, Dielectric barrier discharge, Vacuum plasma
Abstract
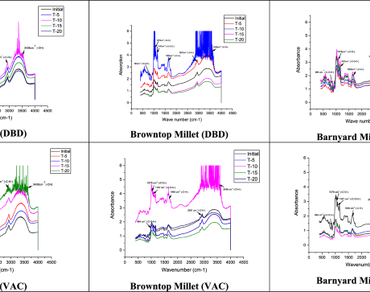
The millet starch treated with dielectric barrier discharge atmospheric plasma and vacuum plasma spectra showed absorption bands at wave number 3436 cm−1 (–O–H–; Vibrational mode starch), 2931 cm−1 & 1650 cm−1 (–C–H–; glucose unit deformation) and 1167 cm−1, 1079 cm−1, 994 cm−1. The compound class alcohol with –O–H– bond stretching is observed in the millet flour at the absorbance range of 3436 cm−1. In comparison to DBD, the vacuum plasma treated millet samples showed more absorption values at wavenumber 3436 cm−1 (–O–H– bond stretching), 1167 cm−1, 1079 cm−1 and 994 cm−1 (–C–O–H–; Stretching vibration). It showed more hydrophilicity of vacuum-treated samples at 10–15 min than DBD. The contact angle formed by DBD showed lesser values than vacuum treated samples. The crystallinity of DBD-treated samples showed a decreasing trend with the course of exposure time.
References
Adebiyi JA, Obadina AO, Mulaba-Bafubiandi AF, Adebo OA, Kayitesi E (2016) Effect of fermentation and malting on the microstructure and selected physicochemical properties of pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum) flour and biscuit. J Cereal Sci 70:132–139
Amita D, Sindhu R, Khatkar BS (2019) Morphological, pasting, and textural characterization of starches and their sub fractions of good and poor cookie making wheat varieties. J Food Sci Technol 56(2):846–853
Apriyanto A, Compart J, Fettke J (2022) A review of starch, a unique biopolymer—structure, metabolism and in planta modifications. Plant Sci 318:111223
Baljeet SY, Ritika BY, Roshan LY (2010) Studies on functional properties and incorporation of buckwheat flour for biscuit making. Int Food Res J 17:1067–1076
Blennow A, Hansen M, Schulz A, Jørgensen K, Donald AM, Sanderson J (2003) The molecular deposition of transgenically modified starch in the starch granule as imaged by functional microscopy. J Struct Biol 143(3):229–241
Chen P, Yu L, Simon G, Petinakis E, Dean K, Chen L (2009) Morphologies and microstructures of cornstarches with different amylose–amylopectin ratios studied by confocal laser scanning microscope. J Cereal Sci 50(2):241–247
Chimphepo L, Alamu EO, Monjerezi M, Ntawuruhunga P, Saka JD (2021) Physicochemical parameters and functional properties of flours from advanced genotypes and improved cassava varieties for industrial applications. LWT 147:111592
Deeyai P, Suphantharika M, Wongsagonsup R, Dangtip S (2013) Characterization of modified tapioca starch in atmospheric argon plasma under diverse humidity by FTIR spectroscopy. Chin Phys Lett 30:018103-1–018103-4
Kikani P, Desai B, Prajapati S, Arun P, Chauhan N, Nema SK (2013) Comparison of low and atmospheric pressure air plasma treatment of polyethylene. Surf Eng 29(3):211–221
Misra NN, Pankaj SK, Segat A, Ishikawa K (2016) Cold plasma interactions with enzymes in foods and model systems. Trends Food Sci Technol 55:39–47
Rui Z, Huilong S, Ruiyang G, Hang L, Shuang L, Chunjian W, Haiming C, Jianfei P, Shanshan G (2024) Supramolecular structure and in vitro digestive properties of plasma-treated corn starches varying in amylose content. Int J Biol Macromol 282(1):136758
Sandhu KS, Singh N, Kaur M (2004) Characteristics of the different corn types 456 and their grain fractions: physicochemical, thermal, morphological and rheological properties of starches. J Food Eng 64:119–127
Shavandi A, Bekhit AA, Bekhit AE, Sun Z, Ali MA (2015) Preparation and characterisation of irradiated crab chitosan and New Zealand Arrow squid pen chitosan. Mater Chem Phys 167:295–302
Thirumdas R, Sarangapani C, Annapure US (2015) Cold plasma: a novel non-thermal technology for food processing. Food Biophys 10:1–11
Thirumdas R, Kadam D, Annapure US (2017) Cold plasma: an alternative technology for the starch modification. Food Biophys 12:129–139
Wongsagonsup R, Deeyai P, Chaiwat W, Horrungsiwat S, Leejariensuk K, Suphantharika M, Fuongfuchat A, Dangtip S (2014a) Modification of tapioca starch by non-chemical route using jet atmospheric argon plasma. Carbohyd Polym 102:790–798
Wongsagonsup R, Pujchakarn T, Jitrakbumrung S, Chaiwat W, Fuongfuchat A, Varavinit S, Fuongfuchat A, Dangtip S, Suphantharika M (2014b) Effect of cross-linking on physicochemical properties of tapioca starch and its application in soup product. Carbohyd Polym 101:656–665
Zhang B et al (2014) Effect of oxygen glow plasma on supramolecular and molecular structures of starch and related mechanism. Food Hydrocoll 37:69–76
Zhang B et al (2015) Understanding the multi-scale structure and functional properties of starch modulated by glow-plasma: a structure-functionality relationship. Food Hydrocoll 50:228–236
Zhang L, Li X, Zhang S, Gao Q, Lu Q, Peng R, Xu P, Shang H, Yuan Y, Zou H (2021) Micro-FTIR combined with curve fitting method to study cellulose crystallinity of developing cotton fibers. Anal Bioanal Chem 413:1313–1320
Author Information
Department of Applied Agriculture, Central University of Punjab, Bathinda, India