Enhanced anti-ageing and wound healing properties of Ficus religiosa L. bark, leaf and aerial root extract in human keratinocytes cell line (HaCaT)
Pandey Prem, Seo Hyo Hyun, Kim Hye-In, Ryu Seung Hwan, Dingre Medini, Moh Sang Hyun, Kulkarni Atul, Parasharami Varsha A.
Research Articles | Published: 21 January, 2020
First Page: 158
Last Page: 165
Views: 4161
Keywords: Anti-ageing, Astringent, Ficus religiosa L., HaCaT, MMP-1, PCOLCE, TERT, Wound healing
Abstract
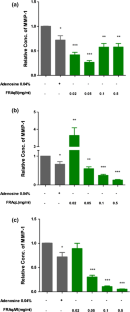
Plants have played a vital role in curative and preventive healthcare. Ficus religiosa L., a medicinally important tree has been used as a traditional medicine to treat various ailments and skin diseases. However, its skin anti-ageing properties are not yet scientifically evaluated. Here we report the comparison of F. religiosa bark (FRAqB), leaf (FRAqL) and aerial-roots (FRAqAR) extracts for skin anti-ageing and wound healing properties. FRAqB, FRAqL and FRAqAR extracts preparation, cell culture, RNA isolation, real time PCR, astringent activity and wound healing assay were carried out using standard methods. Axio Observer FL-microscope and ImageJ software were used for wound healing assay analysis. The real time PCR study reveals that matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MMP) RNA was downregulated to 75% and 95% for FRAqB and FRAqAR, respectively. For procollagen C-endopeptidase enhancer 1 (PCOLCE), FRAqB and FRAqL enhanced RNA levels by 500% and 300%, respectively. FRAqB and FRAqL increased wound healing area to about 60% and FRAqAR by 50%. All three extracts demonstrated astringent activity which is significant for skin tightening. The study proves that extracts of F. religiosa are prominent candidates for pharmaceutical and cosmetic applications such as skin anti-ageing and wound healing.
References
- Ashok PK, Upadhyaya K (2012) Tannins are astringent. J Pharmacogn Phytochem 1:45–50
- Bagyalakshmi B, Nivedhitha P, Balamurugan A (2019) Study on phytochemical analysis, antioxidant and antibacterial activity of Ficus racemosa L. leaf and fruit extracts against wound pathogens. Vegetos 32:58–63
- Brenneisen P, Briviba K, Wlaschek M, Wenk J, Scharffetter-Kochanek K (1997) Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) increases the steady-state mRNA levels of collagenase/MMP-1 in human dermal fibroblasts. Free Radic Biol Med 22:515–524
- Broder C, Arnold P, Goff SV et al (2013) Metalloproteases meprin alpha and meprin beta are C- and N-procollagen proteinases important for collagen assembly and tensile strength. Proc Natl Acad Sci 110:14219–14224
- Choudhary S, Pathak AK, Khare S, Kushwah S (2011) Evaluation of antidiabetic activity of leaves and fruits of Ficus religiosa Linn. Int J Pharm Life Sci 2:1325–1327
- Devi WB, Sengottuvelu S, Haja SS, Lalitha V, Sivakumar T (2011) Memory enhancing activities of Ficus religiosa leaves in rodents. Int J Res Ayurveda Pharm 2:834–838
- Dixit SS, Kulkarni A, Seo HH et al (2016) Anti-oxidant properties of Ficus religiosa L. bark extract on human keratinocytes. Sci Adv Mater 8:1221–1226
- Fisher GJ, Varani J, Voorhees JJ (2008) Looking older: fibroblast collapse and therapeutic implications. Arch Dermatol 144:666–672
- Fisher GJ, Quan T, Purohit T et al (2009) Collagen fragmentation promotes oxidative stress and elevates matrix metalloproteinase-1 in fibroblasts in aged human skin. Am J Pathol 174:101–114
- Fligiel SEG, Varani J, Datta SC, Kang S, Fisher GJ, Voorhees JJ (2003) Collagen degradation in aged/photodamaged skin in vivo and after exposure to matrix metalloproteinase-1 in vitro. J Investig Dermatol 120:842–848
- Flores I, Blasco MA (2010) The role of telomeres and telomerase in stem cell ageing. FEBS Lett 584:3826–3830
- Glöckner G, Scherer S, Schattevoy R, Boright A, Weber J, Tsui LC, Rosenthal A (1998) Large-scale sequencing of two regions in human chromosome 7q22: analysis of 650 kb of genomic sequence around the EPO and CUTL1 loci reveals 17 genes. Genome Res 8:1060–1073
- Gulecha V, Sivakuma T (2011) Anticancer activity of Tephrosia purpurea and Ficus religiosa using MCF 7 cell lines. Asian Pac J Trop Med 4:526–529
- Jagtap S, Gahankari H (2013) Standardization and antimicrobial activity of Ficus Religiosa Linn. (Family: Moraceae). Int Res J Pharm 4:114–117
- Jung HW, Son HY, Minh CV, Kim YH, Park YK (2008) Methanol extract of Ficus leaf inhibits the production of nitric oxide and proinflammatory cytokines in LPS-stimulated microglia via the MAPK pathway. Phytother Res 22:1064–1069
- Kapoor LD (1990) Handbook of ayurvedic medicinal plants. Herbal reference library, 1st edn. CRC Press, New York, pp 149–150
- Kirkpatrick KL, Mokbel K (2001) The significance of human telomerase reverse transcriptase (hTERT) in cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol 27:754–760
- Kumar H, Srivastava SK, Rao CV, Yadav S (2011) Anti-ulcer activity of Ficus religiosa L. leaves on experimental animals. Int J Pharm Sci Rev Res 11:83–86
- Lakshmi HB, Angala PS, Gopinath C (2013) Determination of flavanoidal content by Ficus religiosa Linn leaf extract by TLC and HPTLC. Intl J Pharmacogn Phytochem Res 5:120–127
- Parasharami VA, Vati V, Rabade B, Mehta UJ (2014) Recent antimicrobial and pharmacological studies in Ficus religiosa Linn. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci 3:461–475
- Rajiv P, Sivaraj R (2012) Screening for phytochemicals and antimicrobial activity of aqueous extract of Ficus religiosa Linn. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci 4:207–209
- Sahin E, Depinho RA (2010) Linking functional decline of telomeres, mitochondria and stem cells during ageing. Nature 464:520–528
- Salem MZM, Salem AZM, Camacho LM, Ali HM (2013) Antimicrobial activities and phytochemical composition of extracts of Ficus species: an over view. Afr J Microbiol Res 7:4207–4233
- Shampay J, Blackburn EH (1988) Generation of telomere-length heterogeneity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci 85:534–538
- Singh S, Jaiswal S (2014) Therapeutic properties of Ficus Religiosa. Int J Eng Res Gen Sci 2:150–158
- Singh D, Singh B, Goel RK (2011) Traditional uses, phytochemistry and pharmacology of Ficus religiosa: a review. J Ethnopharmacol 134:565–583
- Singh D, Mukhija M, Sundriyal A, Mangala V (2013) Evaluation of laxative activity of Ficus religiosa Linn. (Moraceae) leaves aqueous extract in albino wistar rats. World J Pharm Pharm Sci 2:5384–5395
- Sprouse AA, Steding CE, Herbert BS (2012) Pharmaceutical regulation of telomerase and its clinical potential. J Cell Mol Med 16:1–7
- Takahara K, Osborne L, Elliott RW, Tsui LC, Scherer SW, Greenspan DS (1996) Fine mapping of the human and mouse genes for the type I procollagen COOH-terminal proteinase enhancer protein. Genomics 31:253–256
- Tongaonkar R, Seo HH, Dixit S, Kulkarni A, Dingre M, Moh SH, Parashrami V (2016) Ficus religiosa L. leaf and aerial root extract induced antioxidant protection in human keratinocytes. Mater Focus 5:571–576
- Warner RL, Bhagavathula N, Nerusu KC, Lateef H, Younkin E, Johnson KJ, Varani J (2004) Matrix metalloproteinase in acute inflammation: induction of MMP-3 and MMP-9 in fibroblasts and epithelial cells following exposure to pro-inflammatory mediators in vitro. Exp Mol Pathol 76:189–195
- Warrier PK, Nambiar VPK, Ramankutty C (1996) Indian medicinal plants: a compendium of 500 species, 3rd edn. Wiley, New York, pp 38–39
- Weinrich SL, Pruzan R, Ma L et al (1997) Reconstitution of human telomerase with the template RNA component hTR and the catalytic protein subunit hTRT. Nat Genet 17:498–502
Author Information
Symbiosis Center for Nanoscience and Nanotechnology (SCNN), Symbiosis International University, Pune, India