Factors regulating the seasonal pattern of microbial and enzyme activities across various land use types in a semi-arid ecosystem of India
*Article not assigned to an issue yet
Research Articles | Published: 15 October, 2025
First Page: 0
Last Page: 0
Views: 111
Keywords: Land use types, Seasonal, Soil microbial activity, Soil enzymatic activity, Soil fertility
Abstract
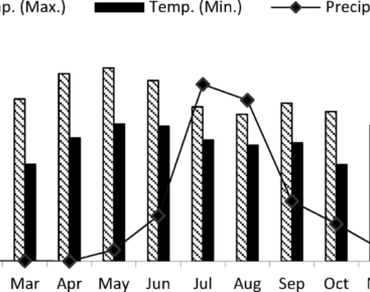
Soil microbes are involved in soil enzyme production, nutrient cycling and respond to land use conversions, soil management practices, soil organic matter (SOM) composition, microclimatic conditions, and soil physicochemical properties. An understanding of these factors helps to make effective strategies to mitigate climate change and ecosystem disturbance. 1) An assessment of seasonal variation in soil physicochemical properties, microbial parameters, and enzyme activities involved in soil carbon (β-glucosidase), nitrogen (urease), phosphorus (acid and alkaline phosphatases) cycles, and oxidation-reduction (dehydrogenase) processes across three different land use types i.e., industrial, agricultural, and forest, in a semi-arid ecosystem of India, and 2) To investigate the factors affecting soil microbial parameters and enzyme activities in these land use types. Seasonal soil samples (pre-monsoon, monsoon and post-monsoon) were collected at a depth of 0-10 cm from different sites at three land use types. Soil physicochemical activity, microbial parameters (basal respiration and substrate-induced respiration) and enzyme activities were assessed using standard methods. The findings indicate that site-specific variations and microclimatic conditions play a significant role in soil nutrient turnover and the decomposition processes that govern seasonal microbial activity and enzyme production. Pearson correlation and principal component analysis revealed that soil nitrogen, moisture, and temperature are the most critical factors influencing microbial respiration and enzyme activities among these ecosystems. This study is more specific to comparative literature that explores the impact of land use and seasonal variations on soil microbiota in the semi-arid ecosystems, which aids in conserving the microbial and physicochemical properties of soil to maintain soil fertility and health.
References
Adam G, Duncan H (2001) Development of a sensitive and rapid method for the measurement of total microbial activity using fluorescein diacetate (FDA) in a range of soils. Soil Biol Biochem 33:943–951. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0038-0717(00)00244-3
Agom O, Gbadebo A (2024) Effects of climate change and global warming on enzymes. RGSA 18(4):e06079. https://rgsa.openaccesspublications.org/rgsa/article/view/6079
Anderson JPE, Domsch KH (1978) A physiological method for the quantitative measurement of microbial biomass in soils. Soil Biol Biochem 10(3):215–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-0717(78)90099-8
Borowik A, Wyszkowska J (2016) Soil moisture as a factor affecting the Microbiological and biochemical activity of soil. Plant Soil Environ 62(6):250–255. https://doi.org/10.17221/158/2016-PSE
Bansal OP, Singh G, Katiyar P (2014) Effect of untreated sewage effluent irrigation on heavy metal content, microbial population and enzymatic activities of soils in Aligarh. J Environ Biol 35(4):641. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25004747
Becerra-Castro C, Lopes AR, Vaz-Moreira I et al (2015) Wastewater reuse in irrigation: a Microbiological perspective on implications in soil fertility and human and environmental health. Environ Int 75:117–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2014.11.001
Chakravarthy D, Raghavendra HV, Ratnam J, Sankaran M (2024) Soil respiration is correlated with rainfall and soil moisture at multiple Temporal scales in a seasonal wet tropical forest. https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.01.03.574121. bioRxiv
Criquet S, Braud A (2008) Effects of organic and mineral amendments on available P and phosphatase activities in a degraded mediterranean soil under short-term incubation experiment. Soil till Res 98(2):164–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2007.11.001
Daunoras J, Kacergius A, Gudiukaite R (2024) Role of soil microbiota enzymes in soil health and activity changes depending on climate change and the type of soil ecosystem. Biology 13(2):85. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology13020085
Eivazi F, Tabatabai MA (1988) Glucosidases and galactosidases in soils. Soil Biol Biochem 20:601–606. https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-0717(88)90141-1
FSI (2021) Forest and tree resources in States and union territories. State of forest report - Rajasthan. Forest Survey of India, Ministry of Environment and Forests, Government of India, Dehradun
Geisseler D, Horwath WR, Scow KM (2011) Soil moisture and plant residue addition interact in their effect on extracellular enzyme activity. Pedobiologia 54:71–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pedobi.2010.11.001
Huang W, Liu J, Zhou G, Zhang D, Deng Q (2011) Effects of precipitation on soil acid phosphatase activity in three successional forests in Southern China. Biogeosciences 8(7):1901–1910. https://doi.org/10.5194/bg-8-1901-2011
Isermayer H (1952) Eine Einpache methode Zur bestimmung der Pflanzenatmung und der Karbonate in boden, Z. Pflanzenernähr. Düng Bodenk 56:26–28. https://doi.org/10.1002/jpln.19520560107
Jian S, Li J, Chen J et al (2016) Soil extracellular enzyme activities, soil carbon and nitrogen storage under nitrogen fertilization: A meta-analysis. Soil Biol Biochem 101:32–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2016.07.003
Kooch Y, Tavakoli M, Akbarinia M (2018) Tree species could have substantial consequences on topsoil fauna: feedback of land degradation/restoration. Eur J Res 137(6):793–805. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10342-018-1140-1
Krämer S, Green DM (2000) Acid and alkaline phosphatase dynamics and their relationship to soil microclimate in a semiarid woodland. Soil Biol Biochem 32(2):179–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0038-0717(99)00140-6
Lan J (2021) Responses of soil organic carbon components and their sensitivity to karst Rocky desertification control measures in Southwest China. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-020-02840-8
Li J, Tong X, Awasthi MK et al (2018) Dynamics of soil microbial biomass and enzyme activities along a chronosequence of desertified land revegetation. Ecol Eng 111:22–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2017.11.006
Liu M, Li P, Liu MM, Wang J, Chang RQ (2021) The trend of soil organic carbon fractions related to the successions of different vegetation types on the tableland of the loess plateau of China. J Soils Sediments 21(1):203–214. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-020-02710-3
Luo Q, Gong J, Zhai Z et al (2016) The responses of soil respiration to nitrogen addition in a temperate grassland in Northern China. Sci Total Environ 569–570:1466–1477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.06.237
Mall RK, Gupta A, Singh R, Singh RS, Rathore LS (2006) Water resources and climate change: an Indian perspective. Curr Sci 90(12):1610–1626
Machuca A, Cuba-Díaz M, Córdova C (2015) Enzymes in the rhizosphere of plants growing in the vicinity of the Polish Arctowski Antarctic station. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 15(4). https://doi.org/10.4067/s0718-95162015005000057
Maestre FT, Delgado-Baquerizo M, Jeffries TC et al (2015) Increasing aridity reduces soil microbial diversity and abundance in global drylands. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112(51):15684–15689. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1516684112
Meena A, Hanief M, Dinakaran J, Rao KS (2020) Soil moisture controls the spatio-temporal pattern of soil respiration under different land use systems in a semi-arid ecosystem of Delhi, India. Ecol Process 9(15). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13717-020-0218-0
Meena A, Rao KS (2021) Assessment of soil microbial and enzyme activity in the rhizosphere zone under different land use/cover of a semiarid region, India. Ecol Process 10(1):1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13717-021-00288-3
Melillo JM, Frey SD, Deangelis KM et al (2018) Long-term pattern and magnitude of soil carbon feedback to the climate system in a warming world. Science 2:101–105. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aan2874
Mir YH, Ganie MA, Shah TI et al (2023) Soil microbial and enzyme activities in different land use systems of the Northwestern Himalayas. PeerJ 11:e15993. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.15993
Olsen SR, Cole CV, Watanabe FS, Dean LA (1954) Estimation of available phosphorus in soils by extraction with sodium bicarbonate. USDA Circular No. 939. US Government Printing Office
Qin H, Xing X, Tang Y et al (2019) Linking soil N₂O emissions with soil microbial community abundance and structure related to the nitrogen cycle in two acid forest soils. Plant Soil 435:95–109. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-018-3863-7
Rawat M, Moturi MC, Subramanian V (2003) Inventory compilation and distribution of heavy metals in wastewater from small-scale industrial areas of Delhi, India. J Environ Monit 5(6):906–912. https://doi.org/10.1039/B306628B
Rubio VE, Detto M (2017) Spatiotemporal variability of soil respiration in a seasonal tropical forest. Ecol Evol 7(17):7104–7116. https://doi.org/10.1002/ece3.3267
Silva EO, de Medeiros EV, Duda GP et al (2019) Seasonal effect of land use type on soil absolute and specific enzyme activities in a Brazilian semi-arid region. CATENA 172:397–407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2018.09.007
Sofi JA, Bhat AG, Kirmai NA et al (2016) Soil quality index as affected by different cropping systems in north-western Himalayas. Environ Monit Assess 188(3):161. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-016-5154-1
Subbiah BV, Asija GL (1956) A rapid procedure for the Estimation of available nitrogen in soils. Curr Sci 25:259–260
Tabatabai MA, Bremner JM (1969) Use of p-nitrophenyl phosphate for assay of soil phosphatase activity. Soil Biol Biochem 1:301–307. https://doi.org/10.1016/0038-0717(69)90012-1
Thalmann A (1968) Zur methodik der bestimmung der Dehydrogenaseaktivität Im Boden mittels Triphenyltetrazoliumchlorid (TTC). Landw Forsch 21:249–258
Uwituze Y, Nyiraneza J, Fraser TD et al (2022) Carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, and extracellular soil enzyme responses to different land use. Front Soil Sci 2:814554. https://doi.org/10.3389/fsoil.2022.814554
Van Leeuwen JP, Djukic I, Bloem J, Lehtinen T, Hemerik L (2017) Effects of land use on soil microbial biomass, activity and community structure at different soil depths in Danube floodplain. Eur J Soil Biol 79:14–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejsobi.2017.02.001
Vinhal-Freitas IC, Corrêa GF, Wendling B, Bobuľská L, Ferreira AS (2017) Soil textural class plays a major role in evaluating the effects of land use on soil quality indicators. Ecol Indic 74:182–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2016
Walkley A, Black IA (1934) An examination of the Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter, and a proposed modification of the chromic acid Titration method. Soil Sci 37(1):29–38. https://doi.org/10.1097/00010694-193401000-00003
Xu CY, Du C, Jian JS et al (2021) The interplay of labile organic carbon, enzyme activities, and microbial communities of two forest soils across seasons. Sci Rep 11:5002. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-84217-6
Yao XH, Min H, Lu ZH, Yuan HP (2006) Influence of Acetamiprid on soil enzymatic activities and respiration. Eur J Soil Biol 42(2):120–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejsobi.2005.12.001
Yuan C, Liang S, Wu X et al (2022) Land use changes influence the soil enzymatic activity and nutrient status in the polluted Taojia river basin in Sub-Tropical China. IJERPH 19(21):13999. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192113999
Author Information
Department of Botany, University of Rajasthan, Jaipur, India