Homology modeling in combination of phylogenetic assortment, a new approach to resolve the phylogeny of selected heterocystous cyanobacteria based on phycocyanin encoding cpcBA-IGS locus
Research Articles | Published: 23 March, 2021
First Page: 339
Last Page: 354
Views: 3754
Keywords: cpcA and cpcB genes, CpcBA-IGS locus, Conserved signature indels, 3-D homology modeling, Phylogeny
Abstract
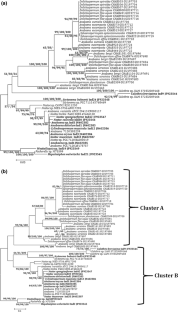
The present communication deals with phylogenetic assessment of phycocyanin coding genes, based on their 3-D structures which is still in its infancy. Homology modeling of cpcA and cpcB in conjunction with molecular phylogenetics for 12 strains belonging to the heterocystous cyanobacteria has been performed with an aim to resolve the ambiguities in their phylogenetic positions. 3D structure has been deduced using Discovery studio while CHIMERA, PEROMALS3D and SALIGN tools have been used for studying the structure based diversity of cpcA and cpcB genes respectively. MEME suite has been further used for motif analysis. Calothrix brevissima Ind9 was the most divergent strain. Nostoc and Anabaena were found to be intermixed at structural level also. The phylogeny suggested monophyletic origin of the heterocystous clade. Conserved Signature Indels provides novel means of identification and also supported monophyletic origin of heterocystous cyanobacteria. At the structure level the secondary elements are more conserved. Overall data obtained through the 3D structure based phylogeny affirmed close association and similar origin of the two subsections. This approach provides better resolution and must be used along with molecular phylogenetics for better identification of cyanobacteria.
References
- Altschul SF, Boguski MS, Gish W, Wootton JC (1994) Issues in searching molecular sequence databases. Nat Gen 6:119–129
- Ballot A, Dadheech PK, Haande S, Krienitz L (2007) Morphological and phylogenetic analysis of Anabaenopsis abijatae and Anabaenopsis elenkinii Nostocales, Cyanobacteria from tropical inland water bodies. Microb Ecol 554:608–618
- Barker GL, Handley BA, Vacharapiyasophon P, Stevens JR, Hayes PK (2000a) Allele-specific PCR shows that genetic exchange occur among genetically diverse Nodularia (Cyanobacteria) filaments in the Baltic Sea. Microbiology 146:2865–2875
- Barker GL, Konopka A, Handley BA, Hayes PK (2000b) Genetic variation in Aphanizomenon (Cyanobacteria) colonies from the Baltic Sea and North America. J Phycol 36:947–950
- Berjanskii M, Zhou J, Liang Y, Lin G, Wishart DS (2012) Resolution-by-proxy: a simple measure for assessing and comparing the overall quality of NMR protein structures. J Biomol NMR 53(3):167–180
- Berman HM, Westbrook J, Feng Z, Gilliland G, Bhat TN, Weissig H, Shindyalov IN, Bourne PE (2000) The protein data bank. Nucl Acids Res 28(1):235–242
- Berrendero E, Perona E, Mateo P (2008) Genetic and morphological characterization of Rivularia and Calothrix (Nostocales, Cyanobacteria) from running water. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 58:447–460
- Bittencourt-Oliveira M-C, Oliveira MC, Bolch CS (2001) Genetic variability of Brazilian strains of the Microcystis aeruginosa complex (cyanobacteria/cyanophyceae) using the phycocyanin intergenic spacer and flanking regions (cpcBA). J Phycol 37:810–818
- Bolch CJ, Blackburn SI, Neilans BA, Grewe PM (1996) Genetic characterization of strains of cyanobacteria using PCR-RFLP of the cpcBA intergenic spacer and flanking regions. J Phycol 32:445–451
- Braberg H, Webb B, Tjioe E, Pieper U, Sali A, Madhusudhan MS (2012) SALIGN: a webserver for alignment of multiple protein sequences and structures. Bioinformatics 28(15):2072–2073
- Buchan DW, Shepherd AJ, Lee D, Pearl FM, Rison SC, Thornton JM, Orengo CA (2002) Gene3D: structural assignment for whole genes and genomes using the CATH domain structure database. Genome Res 12:503–514
- Christiansen G, Molitor C, Philmus B, Kurmayer R (2008) Non-toxic strains of cyanobacteria are the result of major gene deletion events induced by a transposable element. Mol Biol Evol 25:1695–1704
- Colovos C, Yeates TO (1993) Verification of protein structures: patterns of nonbonded atomic interactions. Protein Sci 2(9):1511–1519
- Desikachary TV (1959) Cyanophyta. Monographs on algae. Indian Council of Agricultural Research, New Delhi
- Gouy M, Guindon S, Gascuel O (2010) SeaView version 4: a multiplatform graphical user interface for sequence alignment and phylogenetic tree building. Mol Biol Evol 27(2):221–224
- Gugger MF, Hoffman L (2004) Polyphyly of true branching cyanobacteria (Stigonematales). Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 54:349–357
- Gupta RS (2010) Molecular signatures for the main phyla of photosynthetic bacteria and their subgroups. Photosynth Res 104:357–372
- Haghighi O, Davaeifar S, Zahiri HS et al (2020) Homology modeling and molecular docking studies of glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH) from cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Int J Pept Res Ther 26:783–793
- Howard-Azzeh M, Shamseer L, Schellhorn HE, Gupta RS (2014) Phylogenetic analysis and molecular signatures defining a monophyletic clade of heterocystous cyanobacteria and identifying its closest relatives. Photosynth Res 122:171–185
- Hrouzek P, Lukesová A, Mares J, Ventura S (2013) Description of the cyanobacterial genus Desmonostoc gen. nov. including D. muscorum comb. nov. as a distinct, phylogenetically coherent taxon related to the genus Nostoc. Fottea 13:201–213
- Jones DT (1999) Protein secondary structure prediction based on position-specific scoring matrices. J Mol Biol 292(2):195–202
- Kim SG, Rhee SK, Ahn CY, Ko SR, Choi GG, Bae JW, Park YH, Oh HM (2006) Determination of cyanobacterial diversity during algal blooms in Daechung reservoir, Korea on the basis of the cpcBA intergenic spacer region analysis. Appl Environ Microbiol 72(5):3252–3258
- Komárek J (2013) Cyanoprokaryota. 3. Heterocystous genera. In: Büdel B, Gärtner G, Krienitz L, Schagerl M (eds) Süswasserflora von Mitteleuropa/Freshwater flora of Central Europe. Springer, Heidelberg, p 1130
- Komárek J, Kaštovský J, Mareš J, Johansen JR (2014) Taxonomic classification of cyanoprokaryotes (cyanobacterial genera) using a polyphasic approach. Preslia 86:295–335
- Korelusová J (2008) Phylogeny of heterocystous cyanobacteria (Nostocales and Stigonematales). MSc. Thesis, Faculty of Science, University of South Bohemia, České Budějovice, Czech Republic.
- Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm A, Lopez R, Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG (2007) Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformation 23:2947–2948
- Lee E, Ryan UM, Monis P, McGregor GB, Bath A, Gordon C, Paparini A (2014) Polyphasic identification of cyanobacterial isolates from Australia. Water Res 59:248–261
- Lessel U, Schomburg D (1994) Similarities between protein 3-D structures. Prot Eng 7:1175–1187
- Lovell SC, Davis IW, Arendall WB, de Bakker PIW, Word JM, Prisant MG, Richardson JS, Richardson DC (2002) Structure validation by C alpha geometry: phi, psi and C beta deviation. PROTEINS 50:437–450
- Manen JF, Falquet J (2002) The cpcB-cpcA locus as a tool for the genetic characterization of the genus Arthrospira (Cyanobacteria): Evidence for horizontal transfer. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 52:861–867
- Mishra AK, Shukla E, Singh SS (2013) Phylogenetic comparison among the heterocystous cyanobacteria based on a polyphasic approach. Protoplasma 250:77–94
- Muropastor AM, Kuritz T, Flores E, Herrero A, Wolk CP (1994) Transfer of a genetic marker from a megaplasmid of Anabaena sp. strain PCC7120 to a megaplasmid of a different Anabaena strains. J Bacteriol 176:1093–1098
- Neilan BA, Jacobs D, Goodman AE (1995) Genetic diversity and phylogeny of toxic cyanobacteria determined by DNA polymorphisms within the phycocyanin locus. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:3875–3883
- Pandey S, Srivastava AK, Singh VK, Rai R, Singh PK, Rai S, Rai LC (2013) A new arsenate reductase involved in arsenic detoxification in Anabaena sp. PCC7120. Funct Integr Genom 13:43–45
- Pei J, Kim BH, Grishin NV (2008) PROMALS3D: a tool for multiple protein sequence and structure alignments. Nucleic Acids Res 36(7):2295–2300
- Pettersen EF, Goddard TD, Huang CC, Couch GS, Greenblatt DM, Meng EC, Ferrin TE (2004) UCSF Chimera—a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J Comput Chem 25(13):1605–1612
- Rahman MA, Chaturvedi N, Sinha S, Pandey PN, Gupta DK, Sundaram S, Tripathi A (2013) Computational protein structure modeling and analysis of UV-B stress protein in Synechocystis PCC 6803. Bioinformation 9:639–644
- Rajaniemi P, Hrouzek P, Kastovska K, Willame R, Rantala A, Hoffmann L, Komarek J, Sivonen K (2005) Phylogenetic and morphological evaluation of the genera Anabaena, Aphanizomenon, Trichormus and Nostoc (Nostocales, Cyanobacteria). Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:11–26
- Reehana N, Ahamed AP, Ali DM, Suresh A, Kumar RA, Thajuddin N (2013) Structure based computational analysis and molecular phylogeny of C-phycocyanin gene from the selected cyanobacteria. Int J Biol Biomol Agric Food Biotechnol Eng 7(1):12–16
- Rippka R, Deruelles J, Waterbury JB, Herdman M, Stanier RY (1979) Generic assignments, strain histories and properties of pure cultures of cyanobacteria. J Gen Microbiol 111:1–61
- Schnuchel A, Wiltscheck R, Czisch M, Herrler M, Willimsky G, Graumann P, Marahiel MA, Holak TA (1993) Structure in solution of the major cold-shock protein from Bacillus subtilis. Nature 364(6433):169–171
- Shahi SK, Singh VK, Kumar A, Gupta SK, Singh SK (2013) Interaction of dihydrofolate reductase and aminoglycoside adenyltransferase enzyme from Klebsiella pneumoniae multidrug resistant strain DF12SA with clindamycin: a molecular modelling and docking study. J Mol Model 19(3):973–983
- Shukla E, Singh SS, Mishra AK (2013) Fingerprinting and phylogeny of some heterocystous cyanobacteria using short tandemly repeated repetitive and highly iterated palindrome. Microbiology 82(6):1–8
- Sillitoe I, Lewis TE, Cuff A, Das S, Ashford P, Dawson NL, Furnham N, Laskowski RA, Lee D, Lees JG, Lehtinen S, Studer RA, Thornton J, Orengo CA (2015) CATH: protein structure classification database. Nucleic Acids Res 43(D1):D376–D381
- Singh S, Singh PP (2013) In-silico analysis suggests alterations in the function of XisA protein as a possible mechanism of butachlor toxicity in the nitrogen fixing cyanobacterium Anabaena sp. PCC 7120. Bioinformation 9(13):701–706
- Smith A, Caruso A (2013) In silico characterization and homology modeling of a cyanobacterial phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase enzyme. Struct Biol. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/370820
- Smith AA, Plazas MC (2011) In silico characterization and homology modeling of cyanobacterial phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase enzymes with computational tools and bioinformatics servers. Am J Biochem Mol Biol 1:319–336
- Stoyanov P, Moten D, Mladenov R, Dzhambazov B, Teneva I (2014) Phylogenetic relationships of some filamentous cyanoprokaryotic species. Evol Bioinform 10:39–49
- Tamura K (1992) Estimation of the number of nucleotide substitutions when there are strong transition-transversion and G + C—content biases. Mol Biol Evol 9:678–687
- Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
- Tan W, Liu Y, Wu Z, Lin S, Yu G, Yu B, Li R (2010) cpcBA-IGS as an effective marker to characterize Microcystis wesenbergii (Komárek) Komárek in Kondrateva (cyanobacteria). Harmful Algae 9:607–612
- Taton A, Grubisic S, Brambilla E, De Wilmotte WR (2003) A Cyanobacterial diversity in natural and artificial microbial mats of Lake Fryxell McMurdo Dry Valleys, Antarctica: a morphological and molecular approach. Appl Environ Microbiol 699:5157–5169
- Teneva I, Dzhambazov B, Mladenov R, Schirmer K (2005) Molecular and phylogenetic characterization of Phormidium species (Cyanoprokaryota) using the cpcB-IGS-cpcA locus. J Phycol 41:188–194
- Teneva I, Stoyanov P, Mladenov R, Dzhambazov B (2012) Molecular and phylogenetic characterization of two species of the genus Nostoc (cyanobacteria) based on the cpcB-IGS-cpcA locus of the phycocyanin operon. J Biosci Biotechnol 1(1):9–19
- Valério E, Chambel L, Paulino S, Faria N, Pereira P, Tenreiro R (2009) Molecular identification, typing and traceability of cyanobacteria from freshwater reservoirs. Microbiology 155:642–656
- Wiederstein M, Sippl MJ (2007) ProSA-web: interactive web service for the recognition of errors in three-dimensional structures of proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 35:W407–W410
- Willard L, Ranjan A, Zhang H, Monzavi H, Boyko RF, Sykes BD, Wishart DS (2003) VADAR: a web server for quantitative evaluation of protein structure quality. Nucleic Acids Res 31(13):3316–3319
- Yang S, Valas R, Bourne PE (2009) Evolution studied using protein structure. In: Gu J, Bourne PE (eds) Structural bioinformatics, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York, pp 561–573
Author Information
Laboratory of Microbial Genetics, Department of Botany, Banaras Hindu University, Varanasi, India