Impact of oryzalin on induction of polyploidy in Jasminum sambac (L.) Aiton
*Article not assigned to an issue yet
Vishnupandi S., Ganga S., Manonmani S., Boopathi Manikanda, Swarnalatha P.
Research Articles | Published: 18 August, 2025
First Page: 0
Last Page: 0
Views: 109
Keywords: Polyploidy, Oryzalin, n Jasminum sambacn , Variations
Abstract
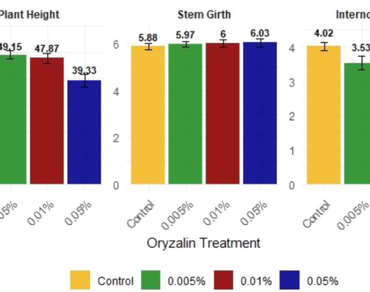
Oryzalin is a potential effective polyploidizing agent, which was employed in the present study for generating high-yielding, commercially viable polyploidy varieties of Jasminum sambac. Rooted cuttings of J. sambac were treated with 0.005%, 0.01%, and 0.05% oryzalin for 6 h under darkness. The survival rate of treated plants indicated that increasing oryzalin concentrations led to a corresponding decrease in survival percentage. The morphological and flowering traits of the treated plants were assessed after 150 days of treatment. The 0.05% oryzalin treatment reduced plant height (39.33 cm) and internodal length (3.46 cm) compared to the control, while increasing stem girth (6.03 mm), leaf area (17.63 cm2), and number of leaves per plant (48.20). The plants treated with 0.05% oryzalin also showed improved floral characteristics, such as flower bud length (2.54 cm) and flower bud girth (2.35 cm). These findings confirm that 0.05% oryzalin may effectively induces polyploidy in J. sambac, producing plants with superior floral characteristics, which hold promise for future breeding programs and the development of novel cultivars. However, further cytological confirmation of ploidy level is essential to validate the stability of the induced polyploids. Once confirmed, these improved lines can serve as valuable genetic resources for developing superior cultivars in future jasmine improvement programs.
References
Behera B (1975) Induced polyploidy in Amaranthus hypochondriacus L. and Amaranthus dubius mart. Ex thell. Cytologia 40(1):157–168
Chen ZJ (2007) Genetic and epigenetic mechanisms for gene expression and phenotypic variation in plant polyploids. Annu Rev Plant Biol 58(1):377–406
Defiani MR, Suprapta D, Sudana I, Ristiati N (2013) Oryzalin treatment modified plant morphology of impatiens balsamina L. Curr World Environ 8(1):23
Eeckhaut TG, Werbrouck SP, Leus LW, Van Bockstaele EJ, Debergh PC (2004) Chemically induced polyploidization in Spathiphyllum Wallisii Regel through somatic embryogenesis. Planr Cell Tissue Organ Cult 78(3):241–246
Ganga M, Rajamani K, Manonmani S, Gnanam R (2022) Impact of pollination strategies on fruit set and fruit growth attributes in Jasmine. J Hortic Sci 17(1):73–82
Ghosh SL (2018) Determination of radio sensitivity of Jasmine (Jasminum spp.) to gamma rays. Electron J Plant Breed 9(3):956–965
Hamill S, Smith M, Dodd W (1992) In vitro induction of banana autotetraploids by Colchicine treatment of micropropagated diploids. Aust J Bot 40(6):887–896
Lan MO, Chen JH, Fei C, Xu QW, Tong ZK, Huang HH, Dong RH, Lou XZ, Lin EP (2020) Induction and characterization of polyploids from seeds of rhododendron Fortunei Lindl. J Integr Agric 19(8):2016–2026
Mata D (2009) New forms of plants produced by polyploidy. Acta horticulture (2009): 813
Mori S, Yahata M, Kuwahara A, Shirono Y, Ueno Y, Hatanaka M, Honda Y, Sugiyama K, Murata N, OkamotoY (2021) Morphological characterization of tetraploids of limonium sinuatum (L.) mill. Produced by Oryzalin treatment of seeds. Horticulturae 7(8):248
Novak A, Jankovic G, Rolovic Z (1992) Two karyotypically unrelated clones with the t (5; 17) and deletion of 5q in myelodysplastic syndrome. Cancer Genet Cytogenet 62(1):100–102
Rose J, Kubba J, Tobutt K (2000) Chromosome doubling in sterile syringa vulgaris× S. pinnatifolia hybrids by in vitro culture of nodal explants. Planr Cell Tissue Organ Cult 63(2):127–132
Silalahi C, Sinuraya M, Hanafiah DS, Sipayung R (2020) The influence of Oryzalin concentrations on the plant growth of two tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) varieties. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science
Sugiyama S (2005) Polyploidy and cellular mechanisms changing leaf size: comparison of diploid and autotetraploid populations in two species of lolium. Ann Botany 96(5):931–938
Vishnupandi S, Ganga M, Rajamani K, Manonmani S, Boopathi NM (2023) Effect of varying concentrations of Colchicine on polyploid induction in Jasminum sambac (L.) Aiton. Electron J Plant Breed 14(2):496–501
Vishnupandi S, Ganga M, Rajamani K, Manonmani S, Shobhana VG, Manikanda Boopathi N (2024a) Floral volatile composition of Jasminum sambac variants developed through Colchicine. Natural Product Research https://doi.org/10.1080/14786419.2023.2298723
Author Information
Department of Agricultural and Horticultural Sciences, School of Agriculture and Food Technology, Vignan’s Foundation for Science, Technology and Research (Deemed to be University), Vadlamudi, India