Lignin Biodegradation in Nature and Significance
Raj Singh, Sushil Kumar Upadhyay, Anju Rani, Permod Kumar, Amit Kumar, Chhaya Singh
Research Article | Published: 11 January, 2019
First Page: 39
Last Page: 44
Views: 4584
Keywords: Lignocellulosic, Biodegradation, Microorganism, Soil fertility, Extracellular enzymes.
Abstract
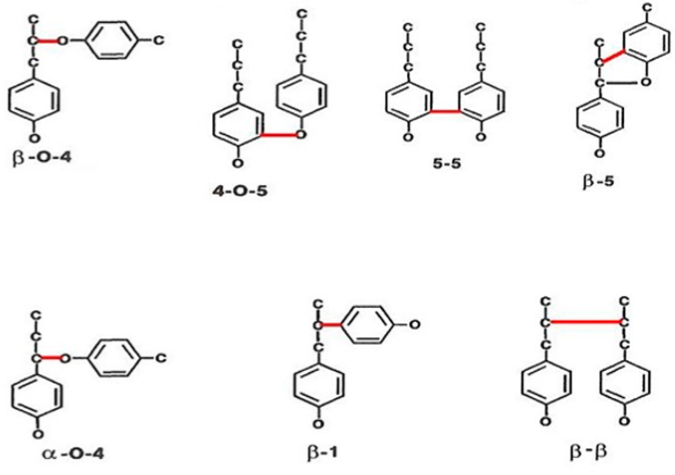
Lignin is the second most abundant aromatic biopolymer next to cellulose constituent of cell wall of vascular plants, where it acts as a structural component of support and conducting tissue. It is recalcitrant to degradation, and creates a barrier towards enzymatic attack by any microbes. It has been identified in primitive groups of plants such as ferns, club mosses and gymnosperms but absent in bryophytes and lower plants. To improve the processing of lignocellulosic feed stocks, humic compound in soil and CO2 Concentration in the environment, it’s required to develop eco-friendly strategies. Lignin degradation has found in nature through the lignolytic enzymes of microbes. Enzymatic degradation of lignin involves five extracellular enzymes- (a) laccase; (b) lignin peroxidase (Lip); (c) manganese-dependent peroxidase (MnP); (d)Versatile peroxidase (VP) and (e) Dye-Decolorizing Peroxidase (DyP). In the present study we discuss the structure of lignin, chemical nature and Enzymology. Authors focus on degradation of lignin through microorganisms found in the plant residues and soil that are capable of producing lignolytic enzymes, which in turn release lignin fractions in soil, hence increase soil fertility through humification.
References
- Adler E (1961) Present status of lignin research. Papier 15 : 604-609.
- Adler E (1977) Lignin chemistry-past, present and future. Wood Sci Technol 11 : 169-218.
- Adler E (1977) Lignin chemistry-past, present and future. Wood Sci Technol 11 : 169-218.
- Ander P and Eriksson KE (1978) Lignin degradation and utilization by micro-organisms. Prog Ind Microbiol 14 : 1-58.
- Ander P and Eriksson KE (1978) Lignin degradation and utilization by micro-organisms. Prog Ind Microbiol 14 : 1-58.
- Ander P and Eriksson KE (1978) Lignin degradation and utilization by micro-organisms. Prog Ind Microbiol 14 : 1-58.
- Apenitis A, Erdtman H and Leopold B (1951) Studies on lignin V. The decay of spruce wood by brown-rotting fungi. Sven. Kem Tidskr 63 : 195-207.
- Argyropoulous DS and Menachem SB (1997) Lignin. In “Advances in Biochemical Engineering and Biotechnology” (Ed. Sheper T) 57 : 127-158. Springer-Verlag, Germany.
- Argyropoulous DS and Menachem SB (1997) Lignin. In “Advances in Biochemical Engineering and Biotechnology” (Ed. Sheper T) 57 : 127-158. Springer-Verlag, Germany.
- Argyropoulous DS and Menachem SB (1997) Lignin. In “Advances in Biochemical Engineering and Biotechnology” (Ed. Sheper T) 57 : 127-158. Springer-Verlag, Germany.
- Bellamy WD (1974) Single cell protein from cellulosic wastes. Biotechnol Bioeng 16 : 869-880.
- Brauns FE (1952) The Chemistry of Lignin. Academic Press, London and New York.
- Brauns FE (1952) The Chemistry of Lignin. Academic Press, London and New York.
- Brauns FE and Brauns DA (1960). The Chemistry of Lignin. Suppl. Vol. Academic Press, New York.
- Bray MW and Andrews TM (1924) Chemical changes of groundwood during decay. Ind Eng Chem 16 : 137-139.
- Brown ME, Barros T and Chang MCY (2012) Identification and characterization of a multifunctional dye peroxidase from a lignin-reactive bacterium. ACS Chem Biol 7: 2074–2081.
- Brown SA (1966) Lignins. Ann Rev Plant Physiol 17 : 223-244.
- Brown W, Cowling EB and Falkehag WI (1968) Molecular size distributions of lignins liberated enzymatically from wood. Sven. Papperstid 22 : 811-821.
- Campbell WG (1952) In “Wood Chemistry” (Eds. Wise LE and EC Jahn). Pp 1061-1116. 2nd ed. Reinhold Publishers Corpn., New York.
- Cartwright KSG and Findlay WPK (1958) Decay of Timber and its Prevention. 2nd Ed. H.M.S.O. London.
- Charaya MU and Singh R (2005) Biochemical Changes in Wheat Crop Residues During their Decomposition in Nature. J Acta Ciencia Indica Vol. XXXI (No. 1). Pp 39-46.
- Chattopadhyay NC and Nandi B (1977) Degradation of cellulose and lignin in malformed mango inflorescence by Fusarium moniliforme var. subglutinens Wr. Rg. Acta Phytopath Acad Sci Hung 12: 283-287.
- Cowling EB (1961) Comparative biochemistry of decay of sweetgum sapwood by white rot and brown rot fungi. USDA Tech Bull 1258.
- Crawford DL and Crawford GL (1976) Microbial degradation of lignocellulose: the lignin component. Appl Environ Microbiol 31: 714-717.
- Crawford DL and Crawford RL (1980) Microbial degradation of lignin. Enz Micro Technol 2: 11-21.
- Crawford RL (1981) Lignin Biodegradation and Transformation. John Wiley and Sons, New York: Chichester, Brisbane, Toronto.
- Crawford RL and Crawford DL (1978) Radioisotopic methods for the study of lignin biodegradation. Dev. Ind. Microbiol 19 : 35-49.
- Dacosta EWB and Benzemer LD (1979) Some techniques for laboratory production of soft rot in wood blocks for experimental purposes. Holzforschung 33: 7-10.
- Dashtban M, Schraft H, Syed TA and Qin W (2010) Fungal biodegradation and enzymatic modification of lignin. Int J Biochem Mol Biol 1(1): 36–50.
- Datta R, Kelkar A, Baraniya D, Molaei A, Moulick A, Meena AS and Formanek P (2017). Enzymatic Degradation of Lignin in Soil. 9(7): 1163.
- Davies DD, Giovanelli J and Rees TA (1964) Plant Biochemistry. Blackwell, Oxford. rot fungi. Physiol Plant 41 : 239-248.
- Drew SW and Kadam KL (1979) Lignin metabolism by Aspergillus fumigatus and white rot fungi. Dev Ind Microbiol 20: 153-161.
- Duncan CG (1960) Wood attacking capacities and physiology of soft rot fungi. USDA Forest Serv Rep 2173 Pp 70.
- Erickson M and Miksche GE (1974a) Two dibenzofurans obtained on oxidative degradation of the moss Polytrichum communa Hedw. Acta Chem Scand B 28: 109-113.
- Erickson M and Miksche GE (1974b) Characterization of gymnosperm lignins by oxidative degradation. Holzforschung 28: 135-138.
- Eslyn WE, Kirk TK and Effland MJ (1975) Changes in the chemical composition of wood caused by six soft rot fungi. Phytopath 65: 473-475.
- Faix O (1991) Classification of lignins from different botanical origins by ft-ir spectroscopy. Holzforschung 45: 21–28.
- Fischer G (1953) Untersuchungen uber den biologischen abbau des Lignins durch Mikroorganismen. Arch Mikrobiol 18: 397-424.
- Fisher AB and Fong SS (2014) Lignin biodegradation and industrial implications. AIMS Bioengg 1(2): 92-112.
- Freudenberg K (1955) In “Modern Methods of Plant Analysis” Vol. 3. (Eds. Peach, K. and M. Tracey), Springer Verlag, Berlin, Gottingen Heidelburg.
- Gonzalo G, Colpa DI, Habib MHM and Fraaije MW (2016) Bacterial enzymes involved in lignin degradation. J Biotech 236: 110-119.
- Gottleib S and Pelczar MJ (1951) Microbiological aspects of lignin degradation. Bacteriol Rev15: 55-76.
- Gottleib S and Pelczar MJ (1951) Microbiological aspects of lignin degradation. Bacteriol Rev 15: 55-76.
- Grohn H and Deters W (1959) Uber den Abbau von Fictenhalz clurch Lenzites saepiaria Holzfoerschung 13 : 8-12.
- Gulyas F (1967) On the role played by several soil fungi in microbiological decomposition of lignin. Agrokem. Talajtan16: 137-150.
- Haider K and Trojanowski J (1975) Decomposition of specifically 14C labelled phenols and dehydropolymers. Arch Microbiol 105 : 33-42.
- Hall PL, Hasser WG and Drew JW (1979) Enzymatic transformation of Lignin. In: Lignin Biodegradation : Microbiology, Chemistry and Application. (Eds. Kirk, T.K. and T. Higuchi) CRC Press, Olereland, Ohio.
- Hatakka A (1994) Lignin-modifying enzymes from selected white rot fungi: production and role in lignin degradation. FEMS Microbiol Rev 13: 125-135.
- Hemmingson JA (1979) A new way of forming lignin-carbohydrate bonds. Etherification of model benzyl alcohols in alcohol/water mixtures. Aust J Chem 32 : 225-229.
- Higuchi T (1971) Formation and biological degradation of lignins. Adv Enzymol 34: 207-283.
- Huang JS (2001) Plant Pathogenesis and Resistance- Biochemistry and Physiology of Plant-Microbe Interactions. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Darbrecht, The Netherland.
- Kaarik AA (1974) Decomposition of wood. In: Biology of Plant Litter Decomposition (Eds. Dickinson CH and GJF Pugh) Academic Press. 1 : 129.
- Kaarik AA (1974) Decomposition of wood. In: Biology of Plant Litter Decomposition (Eds. Dickinson CH and GJF Pugh) Academic Press. 1 : 129.
- Kai D, Tan MJ, Chee PL, Chua YK, Yap YL and Loh XJ (2016). Towards lignin-based functional materials in a sustainable world. Green Chem 18: 1175–1200.
- Keyser P, Kirk TK and Zeikus JG (1978) Lignolytic enzymes system of Phanerochaete chrysosporium Syn in the absence of lignin in response to nitrogen starvation. J Bacteriol 135: 790-797.
- Kirk TK (1971) Effects of microorganisms on lignin. Ann Rev Phytopath 9: 185-210.
- Kirk TK (1975) Effects of a brown rot fungus, Lenzites trabea on lignin in spruce wood. Holzforchung 29: 99-107.
- Kirk TK and Adler E (1970) Methoxyl deficient structural elements in lignin of scocet gum decayed by a brown rot fungus. Acta Chem Scand 24: 3379-3390.
- Kirk TK, Connors WJ and Zeikus JG (1977) Advances in understanding the microbiological degradation of lignin. Rev Adv Phytopath 11: 369-394.
- Kirk TK, Higuchi T and Chang HM (1980) Lignin Biodegradation: Microbiology, Chemistry and Application. CRC Press, West Palm Beach, Fla.
- Kosikova B, Jonaik D and Kosakova L (1979) On the properties of benzyl ether bonds in the lignin-saccharidic complex isolated from spruce. Holzforschung 33: 11-14.
- Kratzl K (1965) Lignin-its biochemistry and structure. In: Cellular ultrastructure of woody plants. Syracuse Univ. Press, Syracuse, New York Pp. 157-180.
- Kremers RE (1959) The Lignins. Ann Rev Plant Physiol 10: 185-196.
- Kuhad RC, Singh A and Karl- Erik L Eriksson (1997) Microorganisms and Enzymes involved in the Degradation of Plant fiber Cell Walls. In: Advances in Biochemical Engineering and Biotechnology (Ed. Scheper, T.) . Springer- Verlag, Germany Pp. 45-125
- Kuhad RC, Singh A and Karl- Erik L Eriksson (1997) Microorganisms and Enzymes involved in the Degradation of Plant fiber Cell Walls. In: Advances in Biochemical Engineering and Biotechnology (Ed. Scheper T) Pp. 45-125. Springer-Verlag, Germany.
- Lawson LR and Still CN (1957) The biological decomposition of lignin- A literature survey. TAPPI 40: 56A-80A.
- Levi MP and Preston RD (1965) A chemical and microscopic examination of the action of the soft rot fungus Chaetomium globosum on beechwood (Fagus sylvatica). Holzforschung 19: 183-190.
- Miksche GE and Yasuda S (1978) Lignin of “giant” mosses and some related species. Phytochem 17: 503-504.
- Moreira PR, Almeida-Vara E, Malcata FX and Duarte JC (2007). Lignin transformation by a versatile peroxidase from a novel Bjerkandera sp. strain. Int Biodeterior Biodegrad 59: 234–238.
- Morrison IM (1979) The degradation and utilization of straw in the rumen. In: Straw Decay and its Effect on Disposal and Utilization (Ed. Grossbard E). John Wiley and Sons. Chichester, New York, Brisbane, Toronto Pp. 237-246.
- Neish AC (1960) Biosynthetic pathways of aromatic compounds . Ann Rev Plant Physiol 11: 55-80.
- Nimz H (1974) Beech lignin-proposal of a constitutional scheme. Angew Chem 86: 336-334.
- Nord FF and de Stevans G (1958) Lignins and lignification. In : Encyclopedia of Plant Physiology ( Ed. Ruhland W) 10: 389-441. Springer Verlag, Berlin.
- Parthasarathi R, Romero RA, Redondo A and Gnanakaran S (2011) Theoretical study of the remarkably diverse linkages in lignin. J Phys Chem Lett 2: 2660–2666.
- Pearl IA (1967) The Chemistry of Lignin. Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York.
- Pearl IA (1967) The Chemistry of Lignin. Marcel Dekker, Inc., New York.
- Pew JC and Weyna P (1962) Fine grinding, enzyme digestion and the lignin-cellulose bond in wood. Tappi 45: 247-256.
- Rani A, Girdharwal V, Singh R, Kumar A and Shukla G (2015). Production of Laccase enzyme by white rot fungi Coriolus versicolor. J Environ Appl Biores 03(04): 204-206.
- Ruiz Dueñas FJ and Martínez AT (2009) Microbial degradation of lignin: how a bulky recalcitrant polymer is efficiently recycled in nature and how we can take advantage of this.Microbial Biotechnol 2(2): 164–177.
- Sarkanen KV (1963) Wood Lignins In: The Chemistry of Wood. (Ed. Bowning BL) Pp. 249-311, Interscience Publishers, New York.
- Savory JG (1954) Breakdown of timber by ascomycetes and Fungi Imperfecti. Ann Appl Biol 41 : 336-347.
- Savory JG and Pinion LC (1958) Chemical aspects of decay of beechwood by Chaetomium globosum. Holzforschung 12 : 99-103.
- Schubert WJ (1965) Lignin Biochemistry. Academic Press, New York.
- Schubert WJ (1973) Lignins. In: Phytochemistry (Ed. Miller LP) Van Nostrand Reinhold Co. 3 :131-153.
- Schubert WJ and Nord FF (1950) Investigations on lignin and lignification. II. The characterization of enzymatically liberated lignin. J Amer Chem Soc 72 : 3835-3838.
- Singh R and Charaya MU (2003) Fungal Colonization of Decomposing Above-Ground Residues of Wheat Crop. Bull Pure Appl Sci 22(1): 55-59.
- Singh R and Charaya MU (2010) Effect of Urea and Single Super Phosphate on In-vitro decomposition of wheat crop residues by Trichoderma Lignorum. Bull Pure Appl Sci 29(2): 63-73.
- Singh R, Charay MU, Shukla L, Shukla G, Kumar A and Rani A (2015b). Lignocellulolytic Potentials of Aspergillus terreus for Management of Wheat Crop Residues. J Acad Indus Res 3(9): 453-455.
- Singh R, Shukla G, Kumar A and Rani A (2015c) Decomposition of Wheat Residues by Fungi. J Acad Indus Res 4 (1); 37-39.
- Singh R, Charaya MU, Amit Kumar, Gyanika Shukla, Anju Rani and Permod Kumar (2015d). Rate of decomposition of plant litter and factor affecting it. Internatl J Biol Sci Biotech Today. 5 (1): 51-55.
- Singh R, Charaya MU, Rani A, Kumar A, Shukla G and Girdharwal V (2015e) Effect of nitrogen and phosphorus in vitro decomposition of wheat crop residue by Stachybotrys atra. Internatl J Sci Res 4(8), 682-683.
- Singh R, Rani A, Kumar A and Girdharwal V (2015a). “Biochemical changes during in vitro decomposition of wheat residue of Trichoderma lignorum (Tode) Harz. Internatl J Adv Inform Sci Technol 4(8): 29-30.
- Singh R, Rani A, Kumar P, Kumar A, Shukla G and Mohd Javed (2016d). Role of microorganism and microfauna in plant litter decomposition. Internatl J Engg Sci Res Technol 5(5): 592-597.
- Singh R, Rani A, Kumar A, Kumar P, Shukla G and Mohd Javed (2016b). Host specific plant litter decomposers in the environment. Global J Res Anal 5(3): 50-52.
- Singh R, Rani A, Kumar P, Shukla G and Kumar A (2016c). The decomposer microorganisms in the environment and their Succession of substrates. Internatl J Engg Sci Res Technol 5(7):1166-1171.
- Singh R, Rani A, Kumar P, Shukla G and Kumar A (2017a). Cellulolytic activity in microorganisms. Bull Pure Appl Sci 36 B (1): 28-37.
- Singh R, Rani A, Kumar P, Shukla G and Kumar A (2017). Hemicellulolytic activity in the crop residues. Internatl J Pharma Res 9(3): 18-20.
- Singh R, Rani A, Kumar P, Sharma A, Shukla G and Kumar A (2016a). Biochemical Changes During Decomposition. Bio Sci Res Bull 32(1): 45-50.
- Singh R and Eltis LD (2015) The multihued palette of dye-decolorizing peroxidases. Arch Biochem Biophys 574,56–65.
- Strittmatter E, Plattner DA and Piontek K (2011). Dye-decolorizing peroxidase (DyP). Encycl Inorg Bioinorg Chem. , 1–13. doi:10.1002/9781119951438.eibc2276
- Sugano Y, Muramatsu R, Ichiyanagi A, Sato T and Shoda M (2007). DyP, a unique dye-decolorizing peroxidase, represents a novel heme peroxidase family: ASP171 replaces the distal histidine of classical peroxidases. J Biol Chem 282: 36652–36658.
- Thurston CF (1994) The Structure and function of fungal laccases. Microbiology 140 : 19-26.
- Vance CP, Kirk TK and Sherwood RT (1980) Lignification as a mechanism of disease resistance. Ann Rev Phytopath 18 : 259-288.
- Waksman SA and Hutchings IJ (1936) Decomposition of lignin by microorganisms. Soil Sci 42 : 119-130.
- Wong DWS (2008) Structure and action mechanism of ligninolytic enzymes. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 157, 174–209.
Author Information
Department of Biotechnology, Maharishi Markandeshwar (Deemed to be University), Mullana- Ambala, Haryana, India.