Nutritional and antinutritional profiling of Indian elephant foot yam [(Amorphophallus paeoniifolius (Dennst.) Nicolson)] genotypes
*Article not assigned to an issue yet
Sarkar Mangaldeep, Gandhi Kelvin, Singh Susheel, Varshney Nitin, Patil Harshal, Patel Brijesh, Chakraborty Binayak, Patel Kamlesh, Karmakar Nilima, Karmakar Nilima
Research Articles | Published: 26 March, 2025
First Page: 0
Last Page: 0
Views: 1408
Keywords: Elephant foot yam, Starch, Ca-oxalate, PC
Abstract
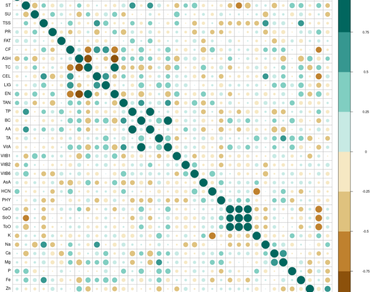
Eighteen elephant foot yam genotypes were analysed for biochemical parameters, were found starch concentration and protein content ranged from 13.90 to 17.89% and 1.08 to 1.95% respectively while more than 30% of the genotypes had protein contents greater than 1.5%. The genotype named Swagata had the highest starch content (17.89%), highest antioxidant activity (17.45 μg/ml; 50% inhibition), Fe (7.45 mg/100 g), and lowest total oxalate (29.70 ppm). The lowest Ca-oxalate (10.20 ppm), soluble oxalate (10.10 ppm), and HCN (30.10 ppm) containing genotype was found to be Gajendra. It also has the highest energy content (371.82 kJ/100 g). STEFYG-4 had the highest protein content (1.95%), whereas CHEFYG-9-2 had the highest beta carotene concentration (336.00 mcg/100 g). Total oxalate and Ca oxalate showed a positive connection (correlation value = 0.929). Micronutrients like Ca and Mg also showed positive correlation. Principle component analysis (PCA) revealed PC3 described 81.66% of the cumulative variability for antinutrient factors, PC5 explained 79.83% of the cumulative variability in biochemical measures. The highest dry matter (31.57%) containing genotype RJEFYG-5 indicated a comparative highest yield potential.
References
Abdullah R (2016) Determination vit C in food samples using high performance liquid chromatography. Chem Mater Res 8(6):8–12
Ahmad MN, Saleemullah M, Shah HU, Khalil IA, Saljoqi AUR (2007) Determination of beta carotene in fresh vegetables using high performance liquid chromatography. Sarhad J Agric 23(3):767–770
AOAC (1990) Official methods of analysis of the association of official analytical chemists. Washington, DC
AOAC (1995) Official methods of analysis of the Association of Official Analytical Chemists. 16th edition Nos. 963.13, 968.08, 970.12, 915.03, 920.87. AOAC, Washington, DC
Bala N, Wilson B, Manju VS, Sundaresan S (2007) Pharmacological properties of Amorphophallus paeoniifolius. In: Root and tuber crops: proceedings of the national seminar on achievements and opportunities in post harvest management and value addition in root and tuber crops (NSTRC2). Central Tuber Crops Research Institute, Thiruvananthapuram, pp 325–328
Bishi SK, Lokesh K, Mahatma MK, Khatediya N, Chauhan SM, Misra JB (2015) Quality traits of Indian peanut cultivars and their utility as nutritional and functional food. Food Chem 167:107–114. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.06.076
Braca A, De Tommasi N, Di Bari L, Pizza C, Politi M, Morelli I (2001) Antioxidant principles from Bauhinia tarapotensis. J Nat Prod 64(7):892–895
Bradbury JH, Holloway WD (1988) Chemistry of tropical root crops: significance for nutrition and agriculture in the Pacific. Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research, Canberra, Australia. No. 435-2016-33750
Burns RE (1971) Method for estimation of tannin in grain sorghum. J Agron 63:511–512
Chattopadhyay A, Saha B, Pal S, Bhattacharya A, Sen H (2010) Quantitative and qualitative aspects of elephant foot yam. Int J Veg Sci 16(1):73–84
Chowdhury B, Hussain M (1979) Chemical composition of the edible parts of aroids grown in Bangladesh. Indian J Agric Sci 49:110–115
Ebun-Oluwa PO, Alade AS (2007) Nutritional potential of Berlandier Nettle spurge (Jatropha cathatica) seed. Pak J Nutr 6(4):345–348
Goering HK, Van Soest PJ (1970) Forage fibre analysis. US Department of Agriculture, Washington, DC, p 379
Hacisalihoglu G, Settles AM (2013) Natural variation in seed composition of 91 common bean genotypes and their possible association with seed coat color. J Plant Nutr. https://doi.org/10.1080/01904167.2012.754041
Hawkesford M, Horst W, Kichey T et al (2012) Functions of macronutrients. In: Marschner P (ed) Marschner’s mineral nutrition of higher plants, 3rd edn. Academic Press, London, pp 135–189
Hedge JE, Hofreiter BT (1962) Methods in carbohydrate chemistry, 17. In: Whistler RL, BeMiller JN (eds) carbohydrate chemistry. Academic Press, New York, p 420
Holloway WD, Argall ME, Jealous WT, Lee JA, Bradbury JH (1989) Organic acids and calcium oxalate in tropical root crops. J Agric Food Chem 37:337–341
Jackson ML (1967) Soil chemical analysis. Prentice Hall of India Private Limited, New Delhi, pp 111–203
Maynard AJ (1970) Methods in food analysis. Academic Press, New York, p 176
Mulualem T, Mekbib F, Hussein S, Gebre E (2018) Analysis of biochemical composition of yams (Dioscorea spp.) landraces from southwest Ethiopia. Agrotech 7:177. https://doi.org/10.4172/2168-9881.1000177
Nedunchezhiyan M (2014) Production potential of intercropping spices in elephant foot yam (Amorphophallus paeoniifolius). Indian J Agron 59:596–601
Purwal L, Shrivastava V, Jain UK (2011) Studies on anti diarrhoeal activity of leaves of Amorphophallus paeoniifolius in experimental animals. Int J Pharm Sci Res 2:468–471
Rahman SS, Hussain MS, Rahman M, Mir MM, Rouf SMA (2021) Nutritional composition and antidiabetic effect of germinated endosperm (Borassus flabellifer), tuber (Amorphophallus paeoniifolius) and their combined impact on rats. Biochem Biophys Rep. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrep.2021.100917
Rajyalakshmi P, Venkatalaxmi K, Venkatalakshmamma K, Jyothsna Y, Balachandramani Devi K, Suneetha V (2001) Total carotenoid and beta-carotene contents of forest green leafy vegetables consumed by tribals of south India. Plant Foods Hum Nutr 56:225–238
Ravi V, Ravindran CS, Suja G, George J, Nedunzhiyan M, Byju G, Naskar SK (2011) Crop physiology of elephant foot yam (Amorphophallus paeoniifolius (Dennst. Nicolson). Adv Hortic Sci 25:51–63
Saikia T, Borah RC (1994) Biochemical composition of acrid and non-acrid amorphophallus corms. J Agric Sci Soc Northeast India 7:90–91
Sakai WS (1983) Aroid root crops: Allocasia, Cyrtospermaand Amorphophallus. In: Chan HT (ed) Handbook of tropical foods. Marcel Dekker, New York, pp 29–83
Santosa E, Sugiyama N, Chozin MA, Lontoh A, Sudiatso S, Kawabata S, Hidayat A (2002) Morphological and nutritional characterization of elephant foot yam in Indonesia. Jpn J Trop Agric 46(4):265–271
Santosa E, Lian CL, Sugiyama N, Misra RS, Boonkorkaew P, Thanomchit K (2017) Population structure of elephant foot yams (Amorphophallus paeoniifolius (Dennst.) Nicolson) in Asia. PLoS ONE 12(6):e0180000. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0180000
Sarkar M, Jadav NK, Chaudhari BN (2024) Swagata: a new high-yielding variety of elephant foot yam. Indian Horticult 69(1):11–14
Shilpi JA, Ray PK, Sarder MM, Uddin SJ (2005) Analgesic activity of Amorphophallus campanulatus tuber. Fitoterapia 76:367–369
Singh N, Awasthi CP, Singh N, Singh NAD (1999) Biochemical composition and nutritive value of promising collections of elephant foot yam (Amorphophallus campanulatus (Roxb)). Veg Sci 26(2):186–187
Singh A, Chaurasiya AK, Mitra S (2016) Assessment of nutritional composition in elephant foot yam (Amorphophallus paeoniifolius Dennst-Nicolson) cultivars. Int J Food Stud 5:146–157. https://doi.org/10.7455/ijfs/5.2.2016.a3
Soobrattee MA, Neergheen VS, Luximon-Ramma A, Aruoma OI (2005) Bahorun T Phenolics as potential antioxidant therapeutic agents: mechanism and actions. Mutat Res Fund Mol Mutagen 579:200–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2005.03.023
Sulnathi G, Prasanthi L, Sekhar MR (2007) Character contribution to diversity in cowpea. Legum Res 30:70–72
Timpa JD, Bruke JJ, Quisenberry JE, Wendt CW (1985) Carbohydrate utilization under stress. Novosibresic USSR 5:65–69
Tränkner M, Tavakol E, Jákli B (2018) Functioning of potassium and magnesium in photosynthesis, photosynthate translocation and photoprotection. Physiol Plant 163:414–431. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.12747
Ulaganathan V, Nirmalakumari A (2015) Multivariate analysis of diversity for qualitative traits in finger millet (Eleusine coracana (L.) Gaertn.) germplasm. Vegetos 28:114–121. https://doi.org/10.5958/2229-4473.2015.00093.2
Wheeler EL, Ferrel RE (1971) A method for phytic acid determination in wheat and wheat fractions. Cereal Chem 48:312–320
Basu SU, Das MO, Sen AN, Choudhury UR, Datta GO (2014) Analysis of complete nutritional profile of amorphophallus campanulatus tuber cultivated in Howrah district of West Bengal, India. Asian J Pharm Clin Res 7(3):25–9
Author Information
Department of Horticulture, College of Agriculture, Navsari Agricultural University, Waghai, The Dangs, India