Phylogenic position and marker studies using cpDNA of C. wightii: A critically endangered and medicinally important plant in India
Research Articles | Published: 18 March, 2021
First Page: 300
Last Page: 308
Views: 5121
Keywords: Commiphora wightii , Endangered species, Chloroplast genome, Phylogenetic analysis
Abstract
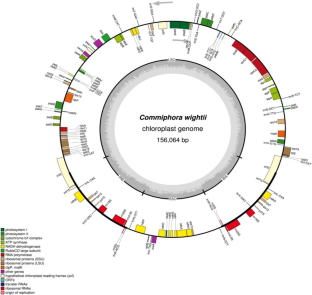
Complete chloroplast genome of Commiphora wightii (family Burseraceae), a medicinally important-critically endangered plant, was assembled using next generation sequencing. Genome annotation was conducted using CpGAVAS web server. The genome is 156,064 bp in length, presenting a typical quadripartite structure of large (LSC; 93,841 bp) and small (SSC; 19,897 bp) single-copy regions separated by a pair of inverted repeats (IRs; 21,163 bp). The genome encodes 125 genes including 86 protein genes, 29 tRNAs, and eight rRNAs. Total 16 simple sequence repeats (SSR), detected in the plastome include the di, tri, tetra, and pentanucleotide repeat. When compared with the plastome of other members of Burseraceae it showed one unique SSR. Total twenty-two hypervariable regions of loci were found in the genome, which could serve as DNA barcodes for species identification. The newly sequenced complete cp genome identified SSRs, nucleotide diversity, phylogenetic analysis, and IR contraction will help in understanding the plastome evolution and genetic conservation of this critically endangered medicinal plant in the future.
References
- Abouelhoda MI, Kurtz S, Ohlebusch E (2004) Replacing suffix trees with enhanced suffix arrays. J Discrete Algorithm 2:53–86
- Barik SK, Tiwari ON, Adhikari D, Singh PP, Tiwary R, Barua S (2018) Geographic distribution pattern of threatened plants of India and steps taken for their conservation. Curr Sci 114:470–503
- Bhatt PP, Thaker VS (2018) The complete chloroplast genome of Cenchrus ciliaris (Poaceae). Mitochondrial DNA Part B 3:674–675
- Dalal KC, Patel MA (1995) Guggal. In: Chadha KL, Gupta R (eds) Advances in horticulture, Vol. 11-medicinal and aromatic plants. Malhotra Publishing House, New Delhi, pp 491–501
- Daniell H, Lin CS, Yu M, Chang WJ (2016) Chloroplast genomes: diversity, evolution, and applications in genetic engineering. Genome Biol 17:134
- Devecchi MF, Thomas WW, Plunkett GM, Pirani JR (2018) Testing the monophyly of Simaba (Simaroubaceae): Evidence from five molecular regions and morphology. Mol Phylogenet Evol 120:63–82
- Dixit AM, Rao SS (2000) Observation on distribution and habitat characteristics of Gugal (Commiphora wightii) in the arid region of Kachchh, Gujarat, India. Trop Ecol 41:81–88
- Dong WL, Wang RN, Zhang NY, Fan WB, Fang MF, Li ZH (2018) Molecular evolution of chloroplast genomes of orchid species: Insights into phylogenetic relationship and adaptive evolution. Int J Mol Sci 19:716
- Fu ZX, Jiao BH, Nie B, Zhang GJ, Gao TG, China Phylogeny Consortium (2016) A comprehensive generic-level phylogeny of the sunflower family: Implications for the systematics of Chinese Asteraceae. J Syst Evol 54:416–437
- Gadek PA, Fernando ES, Quinn CJ, Hoot SB, Terrazas T, Sheahan MC, Chase MW (1996) Sapindales: Molecular delimitation and infraordinal groups. Am J Bota 83:802–811
- Grassi F, Labra M, ScienzaA IS (2002) Chloroplast SSR markers to assess DNA diversity in wild and cultivated grapevines. Vitis 41:157–158
- Gu C, Tembrock L, Zheng S, Wu Z (2018) The complete chloroplast genome of Catha edulis: A comparative analysis of genome features with related species. Int J Mol Sci 19:525
- Gu C, Ma L, Wu Z, Chen K, Wang Y (2019) Comparative analyses of chloroplast genomes from 22 Lythraceae species: inferences for phylogenetic relationships and genome evolution within Myrtales. BMC Plant Biol 19:281
- Guo S, Tembrock L, Zheng S, Wu Z (2018) Complete chloroplast genome sequence and phylogenetic analysis of Paeonia ostii. Molecules 23:246
- Harish GAK, Phulwaria M, Rai MK, Shekhawat NS (2014) Conservation genetics of endangered medicinal plant Commiphora wightii in Indian Thar Desert. Gene 535:266–272
- Hollingsworth PM, Li DZ, van der Bank M, Twyford AD (2016) Telling plant species apart with DNA: from barcodes to genomes. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 371:20150338
- Hu Y, Woeste KE, Zhao P (2017) Completion of the chloroplast genomes of five Chinese Juglans and their contribution to chloroplast phylogeny. Front Plant Sci 7:1955
- Huang H, Shi C, Liu Y, Mao SY, Gao LZ (2014) Thirteen Camellia chloroplast genome sequences determined by high-throughput sequencing: genome structure and phylogenetic relationships. BMC Evol Biol 14:151
- Khan AL, Al-Harrasi A, Asaf S, Park CE, Park GS, Khan AR, Lee IJ, Al-Rawahi A, Shin JH (2017) The first chloroplast genome sequence of Boswellia sacra, a resin-producing plant in Oman. PLoS ONE 12:0169794
- Khan A, Asaf S, Khan AL, Al-Harrasi A, Al-Sudairy O, AbdulKareem NM, Khan A, ShehzadID T, Alsaady N, Al-Lawati A, Al-Rawahi A, Shinwari ZK (2019) First complete chloroplast genomics and comparative phylogenetic analysis of Commiphora gileadensis and C. foliacea: Myrrh producing trees. PLoS ONE 14(1):e0208511
- Kim KJ, Lee HL (2004) Complete chloroplast genome sequences from Korean ginseng (Panax schinseng Nees) and comparative analysis of sequence evolution among 17 vascular plants. DNA Res 11:247–261
- Kuang DY, Wu H, Wang YL, Gao LM, Zhang SZ, Lu L (2011) Complete chloroplast genome sequence of Magnolia kwangsiensis (Magnoliaceae): implication for DNA barcoding and population genetics. Genome 54:663–673
- Kulhari A, Sheorayan A, Kalia S, Chaudhury A, Kalia RK (2012) Problems, progress and future prospects of improvement of Commiphora wightii (Arn.) Bhandari, an endangered herbal magic, through modern biotechnological tools: a review. Genet Resour Crop Evol 59:1223–1254
- Kumar S, Suri SS, Sonie KC, Ramawat KG (2003) Establishment of embryonic cultures and somatic embryogenesis in callus culture of guggul-Commiphora wightii (Arnott.) Bhandari. Indian J Exp Biol 4:69–77
- Lee SR, Choi JE, Lee BY, Yu JN, Lim CE (2018) Genetic diversity and structure of an endangered medicinal herb: implications for conservation. AoB Plants 10:ply021
- Lemieux C, Otis C, Turmel M (2014) Six newly sequenced chloroplast genomes from prasinophyte green algae provide insights into the relationships among prasinophyte lineages and the diversity of streamlined genome architecture in picoplanktonic species. BMC Genom 15:857
- Li Y, Xu W, Zou W, Jiang D, Liu X (2017) Complete chloroplast genome sequences of two endangered Phoebe (Lauraceae) species. Bot Stud 58:37
- Liu C, Shi L, Zhu Y, Chen H, Zhang J, Lin X, Guan X (2012) CpGAVAS, an integrated web server for the annotation, visualization, analysis, and GenBank submission of completely sequenced chloroplast genome sequences. BMC Genomics 13:715
- Lowe TM, Eddy SR (1997) tRNAscan-SE: a program for improved detection of transfer RNA genes in genomic sequence. Nucl Acids Res 25:955–964
- Mitra SK, Kannan R (2007) A note on unintentional adulterations in Ayurvedic herbs. Ethnobot Leafl 2007:3
- Palmer JD, Thompson WF (1982) Chloroplast DNA rearrangements are more frequent when a large inverted repeat sequence is lost. Cell 29:537–550
- Park I, Yang S, Choi G, Kim W, Moon B (2017) The complete chloroplast genome sequences of Aconitum pseudolaeve and Aconitum longecassidatum, and development of molecular markers for distinguishing species in the Aconitum Subgenus Lycoctonum. Molecules 22:2012
- Raman G, Park S (2015) Analysis of the complete chloroplast genome of a medicinal plant, Dianthus superbus var. longi calyncinus, from a comparative genomics perspective. PLoS ONE 10:0141329
- Ravi V, Khurana JP, Tyagi AK, Khurana P (2008) An update on chloroplast genomes. Plant Syst Evol 271:101–122
- Rawat AKS (2005) Importance of quality control of raw material in Ayurvedic medicine. In: Herbal medicine phytopharmaceuticals and other natural products: trends and Advances. Centre for S & T of NAM & other countries and Institute of Chemistry, Ceylon, Sri Lanka, pp 152–158
- Samantaray S, Geetha KA, Hidayath KP, Maiti S (2010) Identification of RAPD markers linked to sex determination in guggal [Commiphora wightii (Arnott.)] Bhandari. Plant Biotechnol Rep 4:95–99
- Sarkinen T, George M (2013) Predicting plastid marker variation: can complete plastid genomes from closely related species help? PLoS ONE 8:e82266
- Terrazas TS (1994) Wood anatomy of the Anacardiaceae-ecological and phylogenetic interpretation. University of North Carolina, Chapel Hill
- Timme RE, Kuehl JV, Boore JL, Jansen RK (2007) A comparative analysis of the Lactuca and Helianthus (Asteraceae) plastid genomes: identification of divergent regions and categorization of shared repeats. Am J Bot 94:302–312
- Twyford AD, Ness RW (2017) Strategies for complete plastid genome sequencing. Mol Ecol Resour 17:858–868
- Ved D, Saha D, Ravikumar K (2015) Commiphora wightii. IUCN Red List Threat Species. https://doi.org/10.2305/IUCN.UK.2015-2.RLTS.T31231A50131117.en
- Vijayan K, Tsou CH (2010) DNA barcoding in plants: taxonomy in a new perspective. Cur Sci 99:1530–1541
- Weeks A, Zapata F, Pell SK, Daly DC, Mitchell JD, Fine PV (2014) To move or to evolve: contrasting patterns of intercontinental connectivity and climatic niche evolution in “Terebinthaceae” (Anacardiaceae and Burseraceae). Front Genet 5:409
- Wu DD, Sha LN, Tang C, Fan X, Wang Y, Kang HY, Zhang HQ, Zhou YH (2018) The complete chloroplast genome sequence of Pseudo roegneria libanotica, genomic features, and phylogenetic relationship with Triticeae species. Biol Plant 62:231–240
- Wyman SK, Jansen RK, Boore JL (2004) Automatic annotation of organellar genomes with DOGMA. Bioinformatics 20:3252–3255
- Xie DF, Yu Y, Deng YQ, Li J, Liu HY, Zhou SD, He XJ (2018) Comparative analysis of the chloroplast genomes of the Chinese endemic genus Urophysa and their contribution to chloroplast phylogeny and adaptive evolution. Int J Mol Sci 19:1847
- Xu J, Feng D, Song G, Wei X, Chen L, Wu X, Li X, Zhu Z (2003) The first intron of rice EPSP synthase enhances expression of foreign gene. Sci China Life Sci 46:561
- Yang M, Zhang X, Liu G, Yin Y, Chen K, Yun Q, Zhao D, Al-Mssallem IS, Yu J (2010) The complete chloroplast genome sequence of date palm (Phoenix dactylifera L.). PLoS ONE 5:12762
- Yang J, Yue M, Niu C, Ma XF, Li ZH (2017) Comparative analysis of the complete chloroplast genome of four endangered herbals of Notopterygium. Genes 8:124
- Yang Z, Wang G, Ma Q, Ma W, Liang L, Zhao T (2019) The complete chloroplast genomes of three Betulaceae species: implications for molecular phylogeny and historical biogeography. PeerJ 7:6320
- Yao X, Tang P, Li Z, Li D, Liu Y, Huang H (2015) The first complete chloroplast genome sequences in Actinidiaceae: genome structure and comparative analysis. PLoS ONE 10:0129347
- You FM, Huo N, Gu YQ, Luo MC, Ma Y, Hane D, Lazo GR, Dvorak J, Anderson OD (2008) BatchPrimer3: a high throughput web application for PCR and sequencing primer design. BMC Bioinform 9:253
- Zhao ML, Song Y, Ni J, Yao X, Tan YH, Xu ZF (2018) Comparative chloroplast genomics and phylogenetics of nine Lindera species (Lauraceae). Sci Rep 8:8844
- Zhou J, Cui Y, Chen X, Li Y, Xu Z, Duan B, Li Y, Song J, Yao H (2018) Complete chloroplast genomes of Papaver rhoeas and Papaver orientale: molecular structures, comparative analysis, and phylogenetic analysis. Molecules 23:437
- Kumar SP (2014) Adulteration and substitution in endangered ASU medicinal plants of India: a review. Int J Med Arom Plants 4(1):56–73.
Author Information
Vimal Research Society for Agro-Biotech and Cosmic Powers, Rajkot, India