Preliminary results of mixed afforestation experiment of Betula alnoides Buch.-Ham. ex D. Don in Southern Fujian China
Chen Bihua, Fang Bijiang, Chen Guobiao, Lin Yuqing, Dai Xinhua, Liao Yinzhen, Hong Xiaolong, Chen Qinggen, Lin Yongjian, Zhang Juan
Research Articles | Published: 20 June, 2020
First Page: 458
Last Page: 465
Views: 4010
Keywords: Betula alnoides buch.-ham. ex d. don, Mixed forest, Tree height, Diameter at breast height (DBH), Volume, Pests and diseases
Abstract
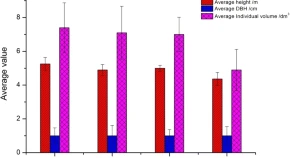
For studying the optimal mixed pattern, the tissue-cultured seedlings of Betula alnoides Buch.-Ham. ex D. Don were introduced to southern Fujian for the mixed afforestation experiments in April 2017. The mixed species were B. alnoides mixed with Cunninghamia lanceolata (Lamb.) Hook. and Castanopsis hystrix Miq., respectively. For mixed forest of B. alnoides and C. hystrix, five treatments were set; for mixed forest of B. alnoides and C. lanceolata, four treatments were set. Two years later the results showed there was no significant difference between different patterns on the tree height, DBH or volume respectively in the mixed forest of B. alnoides and C. hystrix, neither B. alnoides nor C. hystri. There were significant and highly significant differences between different patterns on the tree height, DBH or volume of B. alnoides respectively in the mixed forest of B. alnoides and C. hystrix, but no significant and highly significant differences between different patterns on the tree height, DBH or volume of C. lanceolata respectively. The termites, crickets, longicorn beetles and Lymantria xylina Swinhoe were found damaging B. alnoides in Wanshiqing area, and the L. xylina damaged C. hystrix as well. There were no serious pests or diseases in the mixed forest of B. alnoides and C. lanceolata in Beijing area. The pure forest of B. alnoides was the best to develop in Southern Fujian China.
References
- Chen SX (2013) Study on the biological and ecological characteristics of Betula alnoides’s pest Phalera flavescens. Master Dissertation, Guangxi University, Nanning, China. https://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10593-1013372255.htm
- Chen YH, Zhao ZG, Xu WB, Wang CS, Guo JJ, Li BB, Li XY, Zeng J (2016) Investigation on attack of Arbela spp. to 20 indigenous broad-leaved tree species in Dongjiang Forest Farm, Guangdong Province. J Environ Entomol 38(6):1269–1274. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KCTD201606028.htm
- Huang Y J (2012) Study on the Arbela sp. influence to the Betula alnoide’s texture of material and the insect species in the Betula alnoides forest. Master Dissertation, Guangxi University, Nanning, China. https://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-10593-1012495815.htm
- Liu YL, Pang ZH, Su FB, Li RZ (2012a) Investigation on Lepidarbela baibarana on Betula alnoides. Plant Protect 38(4): 156–158. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZWBH201204038.htm
- Liu YL, Pang ZH, Su FB, Li RZ, Liang L, Huang ML (2012b) Investigation on the damage of Lepidarbela baibarana in the forest of Betula alnoides. Forest Pest Dis 31(3): 26–28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SLBC201203009.htm
- Li ZH (2012) Preliminary study on seedling cultivation technique in Betula alnoides. J Simao Teacher’s College 6:13–18. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SMSG201206005.htm
- Pang SJ, Tang C, Zhang Pei, Jia HY, Zeng J (2016) Attack factors of Arbela spp. in Betula alnoides plantations at Mountain Daqingshan Guangxi. J Northeast For Univ 44(11): 85–88. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DBLY201611018.htm
- Pang ZH (2011) The study progress of Betula alnoides in China. J Guangxi Acad Sci 27(3):243–250. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GXKX201103023.htm
- Wang CS, Zhao ZG, Zeng J, Guo JJ, Sha E, Guo WF, Zeng J, Zheng HS (2013) Relationship between planting density and tree growth process of Betula alnoides Mid-young plantations in Pingxiang Guangxi. Forest Res 26(2): 257–262. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LYKX201302022.htm
- Wang H, Zeng JX, Luo BG, Guo JJ, Wang CS, Zhao ZG, Zeng J (2017) Multiple-trait combined selection of superior Betula alnoides clones in eastern Guangdong. J Central South Univ Forestry Technol 37(12): 72–75. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZNLB201712012.htm
Author Information
Fujian Academy of Forestry Sciences, Fuzhou, China