Synergistic microbial consortia for lignocellulose decomposition in paddy straw
Research Articles | Published: 28 October, 2024
First Page: 2447
Last Page: 2452
Views: 505
Keywords: Microbial degradation, Paddy straw, FE-SEM, Submerged state fermentation, Lignocellulolytic
Abstract
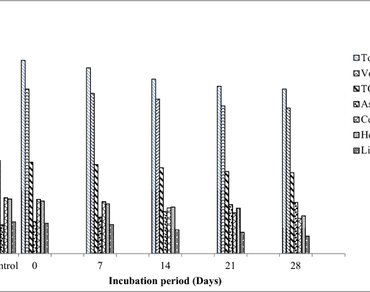
This study investigates the enzymatic degradation of paddy straw (PS) by utilizing submerged state fermentation. Lignocellulolytic ability of six bacterial cultures (isolated from mushroom compost) and one standard culture of Delftia sp. PP4_S3 was evaluated as a consortium to degrade PS. Efficacy of cultures to breakdown lignocellulose was assessed qualitatively, whereby isolate B2 resulted in the highest potency index (PI) of 1.33 for cellulase activity, B6 for hemicellulolytic activity (1.68) and B4 for lignolytic activity (1.32). A synergistic micro-consortia of the isolated and standard culture was used to decompose PS resulting in maximum enzyme activities of endoglucanase (0.79 U/ml), exoglucanase (1.03 U/ml), β-glucosidase (1.59 U/ml), xylanase (11.83 U/ml) and manganese peroxidase (3.84 U/ml) after 21 days of incubation along with laccase (3.77 U/ml) and lignin peroxidase (6.12 U/ml) after 28 days of incubation. By the action of the consortium, PS exhibited a remarkable reduction of 33.51% in cellulose, 20.5% in hemicellulose and 42.72% in lignin content after 28 days of incubation. Structural damage in straw was proven from Field emission scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM). Consequently the use of microbial consortium for biodegradation of PS can be a promising approach to hasten degradation for in-situ management of paddy straw.
References
Ali SS, Al-Tohamy R, Sun J, Wu J, Huizi L (2019) Screening and construction of a novel microbial consortium SSA-6 enriched from the gut symbionts of wood-feeding termite, Coptotermes formosanus and its biomass-based biorefineries. Fuel 236:1128–1145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2018.08.117
AOAC (2000) Official Methods of Analysis, 17th edn. Association of Official Analytical Chemist, Maryland, USA
Arora JK, Singh P, Garg K, Singh M, Aggarwal A, Bala S (2024) Partial replacement of coal with paddy straw pellets as fuel in brick kilns. Biomass Convers Biorefin. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13399-024-06064-5
Arunrat N, Sereenonchai S, Sansupa C, Kongsurakan P, Hatano R (2023) Effect of rice straw and stubble burning on soil physicochemical properties and bacterial communities in central Thailand. Biology 12(4):501
Bozzola JJ, Russell LD (1999) Electron Microscopy: Principles and Techniques for Biologists. Jones and Bartlett, Boston
Carbonero-Pacheco J, Aguilar J, Raya MC, Trapero A, Gaju-Ricart M, Agustí-Brisach C (2023) Diversity of cellulolytic microorganisms associated with the subterranean termite Reticulitermes grassei. J Fungi 9(3):294
Constancio MTL, Sacco LP, Campanharo JC, Castellane TCL, de Oliveira Souza AC, Weiss B, Alves LMC (2020) Exploring the potential of two bacterial consortia to degrade cellulosic biomass for biotechnological applications. Curr Microbiol 77:3114–3124. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-020-02136-7
Devi A, Singh A, Kothari R (2024) Fungi based valorization of wheat straw and rice straw for cellulase and xylanase production. SCENV 5:100077
Dorairaj D, Govender NT (2023) Rice and paddy industry in Malaysia: governance and policies, research trends, technology adoption and resilience. Front Sustain Food Syst 7:1093605
Fukagawa NK, Ziska LH (2019) Rice: importance for global nutrition. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol 65(Supplement):S2–S3
Grgas D, Rukavina M, Bešlo D, Štefanac T, Crnek V, Šikić T, Landeka Dragičević T (2023) The bacterial degradation of lignin—a review. Water 15(7):1272
Jyani M, Palanisamy K, Phutela UG (2024) Characterization and extraction of silica particles from green solvent pretreated paddy straw. Bull Mater Sci 47(3):154
Ma YN, Mongkolthanaruk W, Riddech N (2024) Enhancing soil amendment for salt stress using pretreated rice straw and cellulolytic fungi. Sci Rep 14(1):13903
Mandels M, Anreotti R, Roche C (1976) Measurement of saccharifying cellulase. Biotechnol Bioeng Symp 6:21–23
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal Chem 31:426–428. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac60147a030
Neelkant KS, Shankar K, Jayalakshmi SK, Sreeramulu K (2019) Optimization of conditions for the production of lignocellulolytic enzymes by Sphingobacterium sp. ksn-11 utilizing agro-wastes under submerged condition. Prep Biochem Biotechnol 49(9):927–934. https://doi.org/10.1080/10826068.2019.1643735
Okino LK, Machado KMG, Fabris C, Bononi VLR (2000) Ligninolytic activity of tropical rainforest basidiomycetes. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 16:889–893. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1008983616033
Paszczyński A, Crawford RL, Huynh VB (1988) Manganese peroxidase of Phanerochaete chrysosporium: purification. Meth Enzymol 161:264–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/0076-6879(88)61028-7
Saharan BS, Dhanda D, Mandal NK, Kumar R, Sharma D, Sadh PK, Duhan JS (2024) Microbial contributions to sustainable paddy straw utilization for economic gain and environmental conservation. Curr Res Microb Sci. 7:100264
Singh S, Reddy P, Haarhoff J, Biely P, Janse B (2000) Relatedness of Thermomyces lanuginosus strains producing a thermostable xylanase. J Biotechnol 81:119–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0168-1656(00)00279-0
Sunisa S, Paweena S, Piyangkun L, Suvichark A, Phakhwan T (2024) Isolation and screening of potential lignocellulolytic microbes from Phra Nakhon Si ayutthaya province. J Appl Biol Biotechnol 10(20):1–14. https://doi.org/10.7324/JABB.2024.187833
Tien M, Kirk TK (1988) Lignin peroxidase of Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Meth Enzymol 161:238–249
Toyama N, Ogawa K (1977) International Course on Biochemical Engineering and Bioconversion. In: Ghose TK (ed) Biochem Eng Research Centre. IIT, New Delhi India, p 182
Turner EM (1974) Phenoloxidase activity in relation to substrate and development stage in the mushroom. Agaricus Bisporus T Brit Mycol Soc. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0007-1536(74)80103-8
Verma I, KATYAL P, (2024) Microbial degradation of paddy (Oryza sativa) straw by submerged state fermentation. Indian J Agric Sci 94(8):908–911
Zheng G, Yin T, Lu Z, yannickbenzBoboua S, Li J, Zhou W, (2020) Degradation of rice straw at low temperature using a novel microbial consortium LTF-27 with efficient ability. Bioresour Technol 304:123064. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2020.123064
Author Information
Department of Microbiology, College of Basic Sciences and Humanities, Punjab Agricultural University, Ludhiana, India