Assessment of physico-chemical properties of pre and post-treated wastewater of Prayagraj region and its effect on nearby Ganges river
Adbarzi Soad Shaban Mohamed, Tripathi Pooja, Choudhary Krishna Kumar, Kant Rajiv
Research Articles | Published: 31 January, 2020
First Page: 258
Last Page: 264
Views: 4141
Keywords: Physico-chemical parameter, Wastewater, Municipal wastewater treatment plants, Ganges river
Abstract
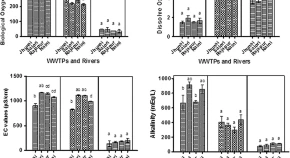
Safe discharge of wastewater is still a difficult problem in every part of the world mainly in developing countries. The discharge of wastewater affects the physicochemical properties of receiving water streams and soil which enters into the food chain and affects agriculture products, animal and human health. The present study was focused on the physicochemical properties of pre and post-treated wastewater samples from 04 different municipal wastewater treatment plants (WWTP) of Jhunsi (16 MLD), Salori (29 MLD), Rajapur (60 MLD), Naini (80 MLD) and their receiving Ganges river in Prayagraj (Allahabad), India. Water quality parameters such as pH, total dissolved solid (TDS), dissolved oxygen (DO), electrical conductivity (EC), turbidity, biological oxygen demand (BOD), chemical oxygen demand (COD), chloride and total hardness were analyzed. All parameters investigated were analyzed using standard methods. The results indicated that the WWTPs of Prayagraj region were effectively working and reducing the TDS, BOD and COD to acceptable limits.
References
- Abdullah WN, Lau WJ, Aziz F, Emadzadeh D, Ismail AF (2018) Performance of nanofiltration-like forward-osmosis membranes for aerobically treated palm oil mill effluent. Chem Eng Technol 41(2):303–312
- Bethi B, Sonawane SH, Bhanvase BA, Gumfekar SP (2016) Nanomaterialsbased advanced oxidation processes for wastewater treatment: a review. Chem Eng Process 109:178–189
- Fatta-kassinos D, Kalavrouziotis I, Koukoulakis P (2011) The risks associated with wastewater reuse and xenobiotics in the agroecological environment. Sci Total Environ 408(19):3555
- Gatica J, Tripathi V, Green S, Manaia C, Berendonk T, Merlin C, Kreuzinger N, Schwartz T et al (2016) High throughput analysis of class 1 integron gene cassettes in wastewater environments. Environ Sci Technol 50(21):11825–11836
- Gatta G, Libutti A, Gagliardi A, Beneduce L, Brusetti L, Borruso L, Disciglio G, Tarantino E (2015) Treated agro-industrial wastewater irrigation of tomato crop: effects on qualitative/quantitative characteristics of production and microbiological properties of the soil. Agric Water Manag 149:33–43
- Grey D, Garrick D, Blackmore D, Kelman J, Muller M, Sadoff C (2013) Water security in one blue planet: twenty-first century policy challenges for science. Philos Trans R Soc Lond A Math Phys Eng Sci 371:201–204
- Indian Standards for Drinking Water—Specification (Bis 10500: 1991) IS: 2296 (1982) Tolerance limits for inland surface waters subject to pollution
- Kesari KK, Tripathi P, Tripathi V (2018) Influence of wastewater use in agriculture: advances in human and plant health. Adv Microb Biotechnol 1:232–246
- Malki M, Bouchaou L, Mansir I, Benlouali H, Nghira A, Choukr-Allah R (2017) Wastewater treatment and reuse for irrigation as alternative resource for water safeguarding in Souss-Massa region, Morocco. Eur Water 59:365–371
- Mbalassa M, Bagalwa M, Nshombo M, Kateyo M (2014) Assessment of physicochemical parameters in relation with fish ecology in Ishasha River and Lake Edward, Albertine Rift Valley, East Africa. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl 3:230
- Mohr KF (2006) Neue massanalytische Bestimmung des Chlors in Verbindungen. Ann Chem Pharm 97:335–338. https://doi.org/10.1002/jlac.18560970314
- Naidoo S, Olaniran AO (2013) Treated wastewater effluent as a source of microbial pollution of surface water resources. Int J Environ Res Public Health 11(1):249
- Nirgude NT, Shukla S, Venkatachala A (2013) Physico-chemical analysis of some industrial effluents from Vapi Industrial Area, Gujarat, India. RACAYAN J Chem 6(1):68–72
- Odjadjare EEO, Igbinosa EO, Okoh AI (2011) Microbial and physicochemical quality of an urban reclaimed wastewater used for irrigation and aquaculture in South Africa. Afr J Microbiol Res 5(15):2179
- Raji MIO, Ibrahim YKE, Tytler BA, Ehinmidu JO (2015) Physicochemical characteristics of water samples collected from River Sokoto, Northwestern Nigeria. Atmos Climate Sci 5(03):194
- U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (1975) Interim primary drinking water standards. Federal Register 40(51):11990
- Reda AH (2016) Physico-chemical analysis of drinking water quality of Arbaminch Town. J Environ Anal Toxicol 6(2):1–5. https://doi.org/10.4172/2161-0525.1000356
- Salem IB, Ouardani I, Hassine M, Aouni M (2011) Bacteriological and physico-chemical assessment of wastewater in different region of Tunisia: impact on human health. BMC Res Notes 4(1):1
- Sangu RPS, Sharma SK (1987) An assessment of water quality of river Ganga at Garmukeshwar. Ind J Ecol 14(20):278–287
- Sawyer CN, McCarty PL, Parkin GF (2000) Chemistry for environmental engineering, 4th edn. McGraw-Hill Inc, New York
- Suriyaprabha R, Fulekar MH (2018) Study on the physico-chemical parameters of dye industry effluents from industrial Estate Vatva, Ahmedabad, Gujarat. Int J Adv Eng Res Dev 5(3):1706–1710
- Tawari-Fufeyin P, Paul M, Godleads AO (2015) Some aspects of a historic flooding in Nigeria and its effects on some Niger-Delta communities. Am J Water Resour 3(1):7–16. https://doi.org/10.12691/ajwr-3-1-2
- Teklehaimanot GZ, Genthe B, Kamika I, Momba MNB (2015) Prevalence of enteropathogenic bacteria in treated effluents and receiving water bodies and their potential health risks. Sci Total Environ 518:441
- The US Salinity Laboratory Staff (1954) Diagnosis and improvement of saline and alkali soils, USDA Handbook 60, Washington DC
- Tripathi V, Cytryn E (2017) Impact of anthropogenic activities on the dissemination of antibiotic resistance across ecological boundaries. Essay Biochem 61(1):11–21
- Trivedy RK, Goel PK (1986) Chemical and biological method for water pollution studies. Environ Publ (Karad, India) 6:10–12
- Wang YC, Peng YA, Li YM (2004) The characteristics of water pollution and engineering-oriented prevention on Dianchi. Areal Res Dev 23:88–92
- WHO (2006) Guidelines for the Safe use of wastewater, volume 2: wastewater use in agriculture. World Health Organization, Geneva
- WHO (2011) Guidelines for drinking-water quality, 4th edn
Author Information
Department of Molecular and Cellular Engineering, Jacob Institute of Biotechnology and Bioengineering, Sam Higginbottom University of Agriculture, Technology and Sciences, Prayagraj, India