Cultural, pathogenic and genetic variability of Rhizoctonia solani isolates incitant of rice sheath blight disease
*Article not assigned to an issue yet
Sandhya Y., Kumar M. Reddi, Madhusudhan P., Sudhakar P., Kumari P. Lavanya
Research Articles | Published: 20 January, 2026
First Page: 0
Last Page: 0
Views: 116
Keywords: n Rhizoctonia solanin , Variability, Anastomosis groups, Sclerotia
Abstract
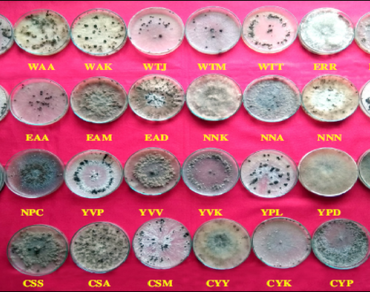
Thirty isolates of Rhizoctonia solani collected from various rice varieties grown in different regions of Andhra Pradesh were studied for their cultural, pathogenic and molecular variability. Many of the isolates were moderate growers while ten were fast growers. Colony color varied from white to brown. Hyphal width varied from 13.59 to 31.66 μm. The color of sclerotia was initially white and dark brown with maturity. While sclerotia number ranged between 3 and 89 with different patterns, their size varied between 0.8 and 2.8 mm. The virulence of each pathogen isolate was studied on three rice varieties, that is NLR-34449 (susceptible), IR-64 (moderately susceptible), Tetep (moderately resistant) in glasshouse, and observations were recorded by measuring the relative lesion height. The relative lesion heights of these isolates on three rice varieties varied widely based on which the isolates could be grouped as highly virulent, moderately virulent and less virulent. The RLH on NLR-34449 ranged from the lowest 15.13% to the highest 54.66%, on IR- 64 from the lowest 5.73% to the highest 49.03% and Tetep from the lowest 2.00% to the highest 38.46% by the isolates EAD (lowest) and WAK (highest), respectively. There was no relationship between culturally similar isolates and their pathogenic behavior. Genetic variation of the isolates was analyzed using RAPD markers. The primers OPA-07, OPA-10, OPC-11, OPC-19, OPB-17, OPE-06, OPF-14 and OPG-11were informative and given polymorphism among the isolates. The PIC (Polymorphic Information Content) values ranged from 0.36 (OPC-11) to 0.49 (OPG-11) with an average PIC value of 0.44. Largely, grouping of the isolates happened based on their geographical origin.
References
Bhunkal N, Singh R, Mehta N (2015) Assessment of losses and identification of slow blighting genotypes against sheath blight of rice. J Mycol Pl Pathol 45:285–292
Chen J, Wang C, Canwei S, Zhu M, Zhou E (2015) Isolation and characterization of a melanin from Rhizoctonia solani, the causal agent of rice sheath blight. Eur J Plant Pathol 142(2):281–290
DeRiek J, Calsyn E, Everaert I, Van Bockstaele E, De Loose M (2001) AFLP-based alternatives for the assessment of distinctness, uniformity and stability of sugar beet varieties. Theor Appl Genet 103:1254–1265
Esfahani MN (2020) Genetic variability and virulence of some Iranian Rhizoctonia solani isolates associated with stem canker and black scurf of potato (Solanum tuberosum L.). J Plant Prot Res 60(1):21–30. https://doi.org/10.24425/jppr.2020.132201
Forghani D, Bazgir E, Nasr Esfahani M, Darvishnia M (2021) Genomic structure of novel Iranian Rhizoctonia solani AG-3PT isolates on potato, Solanum tuberosum. Sydowia 73:217–229
Gopireddy BM, Uma Devi G, Vijayakrishna KK, Babu RT, Naidu TCM (2017) Cultural and morphological characterization of Rhizoctonia solani f. sp. sasakii isolates collected from different districts of Andhra Pradesh. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci 6(11):3457–3469
Guleria S, Aggarwal R, Thind TS, Sharma TR (2007) Morphological and pathological variability in rice isolates of Rhizoctonia solani and molecular analysis of their genetic variability. J Phytopathol 155:654–661
Hejazi R, Esfahani MN, Maleki M, Sedaghatfar E (2022) Susceptibility assessment and genetic population structure associated with Rhizoctonia solani AG3-PT - potato stem canker disease. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 119:101835. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmpp.2022.101835
Khodayari M, Naser S, Masoud S (2009) Genetic diversity of iranian AG1-IA isolates of Rhizoctonia solani, the cause of rice sheath blight, using morphological and molecular markers. J Phytopathol 157:708–714
Kumar RM, Balasubramanian KA (2007) Genetic relatedness, susceptibility and resistant leaves of different black gram genotypes to leaf spot fungus, Corynespora cassiicola. J Mycol Pl Pathol 37(1):101–104
Lawson JA, Harris JW, Ballal SK (1973) Application of computer analysis of electrophoretic banding patterns of enzymes to the taxonomy of certain wood –rotting fungi. Taxon Wood Rotting Fungi Econ Bot 29(2):117–125
Lee FN, Rush MC (1983) Rice sheath blight: a major rice disease. Plant Dis 67(7):829–832
Lieberman GJ, Owen DB (1961) Tables of hypergeometric probability distribution. Stanford University Press, pp 726
Manjunatha O, Vidya Sagar B, Prakasam V, Narendra Reddy CN (2018) Variability studies on sheath blight of rice in Karnataka, India. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci 7(10):724–736
McDonald BA, Linde C (2002) Pathogen population genetics, evolutionary potential, and durable resistance. Annu Rev Phytopathol 40:349–379
Monazzah A, Esfahani MN, Enferadi ST (2022) Genetic structure and proteomic analysis associated in potato to Rhizoctonia solani AG-3PT-stem canker and black scurf. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 122:101905. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmpp.2022.101905
Munsell’s Soil Colour Chart (1954) Munsell Colour Co. Inc. Baltimore, Maryland, USA
Murray MG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8:4321–4325
Raju K (1999) Investigations into the variation in Corynyspora cassicola incitant of leaf spot of Black gram (Vigna mungo L. Hepper). M. Sc. Thesis. Professor Jayasankar Telangana State Agricultural University, pp 128–129
Rangaswami G, Mahadevan A (1999) Diseases of crop plants in India, 4th edn. Prentice Hall of India Pvt Ltd, New Delhi, p 607
Sha XY, Zhu LH (1990) Resistance of some rice varieties to sheath blight (ShB). Int Rice Res Newsletter 15:7–8
Singh V, Singh US, Major S, Kumar A (2002) Genetic diversity of Rhizoctonia solani isolates from rice: differentiation by morphological characteristics, pathogenicity, anastomosis behaviour and RAPD finger printing. J Mycol Plant Pathol 32(3):332–344
Singh SK, Shukla V, Singh H, Sinha AP (2004) Current status and impact of sheath blight in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Agric Rev 25(4):289–297
Soheili BM, Sedigheh M, Nasr EM, Hamed HK, Houssein KK (2022) Identification of novel associations of candidate genes with resistance to Rhizoctonia solani AG-3PT in Solanum tuberosum stem canker. Int J Biol Macromol 215:321–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.06.105
Soheili BM, Nasr EM, Mousanejad S (2023) Biochemical defense mechanism associated with host-specific disease resistance pathways against Rhizoctonia solani AG3-PT potatoes canker disease. Planta 257:13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-022-04039-2
Vidhyasekaran P, Ruby Ponmalar T, Samiyappan R, Velazhahan R, Vimala R, Ramanathan A, Paranidharan V, Muthukrishnan S (1997) Host-specific toxin production by Rhizoctonia solani, the rice sheath blight pathogen. Biochemistry and cell biology. Am Phytopathol Soc 87(12):1258–1263
Wang L, Liu LM, Wang ZG, Huang SW (2013) Genetic structure and aggressiveness of Rhizoctonia solani AG1-IA, the cause of sheath blight of rice in Southern China. J Phytopathol 161:753–762
Xiao Y, Liu M, Li G, Zhou E, Wang L, Tang J, Tan F, Zheng A, Li P (2008) Genetic diversity and pathogenicity variation in Rhizoctonia solani isolates from rice in sichuan province, China. Rice Sci 15:137–144
Yugander A, Ladhalakshmi D, Prakasham V, Mangrauthia S K, Prasad M S, Krishnaveni D, Madhav M S, Sundaram R M, Laha G S (2014) Pathogenic and genetic variation among the isolates of Rhizoctonia solani (AG 1-IA), the rice sheath blight pathogen. J Phytopathol 1–10
Zhou EX, Cao JX, Yang M, Zhu XR (2002) Studies on the genetic diversity of Rhizoctonia solani AG-1-IA from six provinces in the southern China. J Nanjing Agric Univ 3:36–40
Zuo SM, Wang ZB, Chen XJ, Gu F, Zhang YF, Chen ZX, Pan XB, Pan CH (2009) Evaluation of resistance of a novel rice line YSBR1 to sheath blight. Acta Agron Sin 35:608–614
Rani N S, Prasad G S V, Rao LVS (2008) High yielding rice varieties of India. Technical Bulletin No. 33, Directorate of Rice Research, Rajendranagar. Hyderabad 500030, Andhra Pradesh, India, pp 188
Author Information
Department of Plant Pathology, S.V. Agricultural College, ANGRAU, Tirupati, India