Structural characterization of phenolic content, antioxidant and antibacterial activities of Coffea arabica green seeds
Aissaoui Mohammed, Rahmoun Nadjib Mohammed, Barek Said, Bensouici Chawki, El Haci Imad Abdelhamid
Research Articles | Published: 21 June, 2020
First Page: 466
Last Page: 474
Views: 4171
Keywords: Coffea arabica green seeds, RP-HPLC-PDA, Antioxidant activity, Antibacterial activity
Abstract
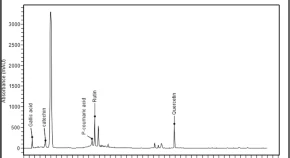
This study concerns the evaluation of the antioxidant and antibacterial activities of Coffea arabica green seed extract. The chemical compositions were analyzed by RP-HPLC-PDA spectroscopy. Antioxidant activities were assessed using 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl scavenging, 2,2′-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid), reducing power and phenanthroline assays. The antibacterial activity was tested against 14 bacterial strains as per CLSI recommendation. The RP-HPLC-PDA revealed the presence of resorcinol, ferulic acid, rutin, catechin, gallic acid, caffeic acid, quercetin, chlorogenic acid and p-coumaric acid. The n-butanolic extract has the highest activity with 2,2-diphenyl-1-picryl-hydrazyl-hydrate (20.09 ± 0.40 µg/ml) and 2,2′-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) (5.27 ± 0.19 μg/ml) assays. The A0.5 of the methanolic crude extract was 8.18 ± 0.63 μg/J ml for reducing power and 2.54 ± 0.06 μg/ml for phesnanthroline assay. The n-butanol extract showed an interesting antibacterial activity against Citrobacter freundii ATCC 8090 and Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 6538 with minimal inhibitory concentration of 13.02 µg/ml. Our finding provides an effective and specific natural approach to search for classes of antioxidant and antibacterial compounds for different uses.
References
- Alam P, Parvez MK, Arbab AH, Al-Dosari MS (2017) Quantitative analysis of rutin, quercetin, naringenin, and gallic acid by validated RP- and NP-HPTLC methods for quality control of anti-HBV active extract of guiera senegalensis. Pharm Biol 55:1317–1323
- Amri O, Elguiche R, Tahrouch S, Zekhnini A, Hatimi A (2015) Antifungal and antioxidant activities of some aromatic and medicinal plants from the southwest of Morocco. J Chem Pharm Res 7:672–678
- Ang AMG, Enot MM, Baltazar GJD, Alinapon CV, Buncales EO, Barbosa GB (2019) Antioxidant and cytotoxic activity of the leaf ethanolic extracts of Tithonia diversofilia and Gliricidia sepium from Bukidnon, Philippines. AJBLS 8:8–15
- Babova O, Occhipinti A, Maffei ME (2016) Chemical partitioning and antioxidant capacity of green coffee (Coffea arabica and Coffea canephora) of different geographical origin. Phytochemistry 123:33–39
- Barek S, Rahmoun NM, Aissaoui M, El Haci IA, Bensouici C, Choukchou-Braham N (2020) Phenolic contents, antioxidant, and antibacterial activities of the Algerian Genista saharae solvent extracts. J Herbs Spices Med Plants 26:1–13
- Basli A, Chibane M, Madani K, Oukil N (2012) Activité antibactérienne des polyphénols extraits d’une plante médicinale de la flore d’Algérie: Origanum glandulosum Desf. Phytothérapie 10:2–9
- Bhalodia NR, Nariya PB, Acharya RN, Shukla VJ (2013) In vitro antioxidant activity of hydro alcoholic extract from the fruit pulp of Cassia fistula Linn. Ayu 34:209–214
- Bhupathiraju SN, Pan A, Malik VS, Manson JE, Willett WC, Van Dam RM, Hu FB (2012) Caffeinated and caffeine-free beverages and risk of type 2 diabetes. Am J Clin Nutr 97:155–166
- Blois MS (1958) Antioxidant determinations by the use of a stable free radical. Nature 181:1119–1200
- Bouarab Chibane L, Degraeve P, Ferhout H, Bouajila J, Oulahal N (2019) Plant antimicrobial polyphenols as potential natural food preservatives. J Sci Food Agric 99:1457–1474
- Cano-Marquina A, Tarín JJ, Cano A (2013) The impact of coffee on health. Maturitas 75:7–21
- Chandran H, Meena M, Barupal T, Sharma K (2020) Plant tissue culture as a perpetual source for production of industrially important bioactive compounds. Biotechnol Rep 26:e00450
- Cheng Z, Ren J, Li Y, Chang W, Chen Z (2002) Study on the multiple mechanisms underlying the reaction between hydroxyl radical and phenolic compounds by qualitative structure and activity relationship. Bioorg Med Chem 10:4067–4073
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (2012) Methods for dilution antimicrobial susceptibility tests for bacteria that grow aerobically, 9th edn. Approved standard M07-A9. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, Wayane
- Dar RA, Brahman PK, Khurana N, Wagay JA, Lone ZA, Ganaie MA, Pitre KS (2017) Evaluation of antioxidant activity of crocin, podophyllotoxin and kaempferol by chemical, biochemical and electrochemical assays. Arab J Chem 10:S1119–S1128
- Demkura PV, Ballaré CL (2012) UVR8 mediates UV-B-induced Arabidopsis defense reponses against Botrytis cinerea by controlling sainapate accumulation. Mol Plant 5:642–652
- Ebrahimi NS, Hadian J, Mirjalili MH, Sonboli A, Yousefzadi M (2008) Essential oil composition and antimibacterial activity of Thymus caramanicus at differents phonologicals stages. Food Chem 110:927–931
- El Haci IA, Mazari W, Atik-Bekkara F, Mouttas-Bendimerad F, Hassani F (2020) Bioactive compounds from the flower part of Polygonum maritimum L. collected from Algerian coast. Curr Bioact Compd 16:543–545
- Falleh H, Ksouri R, Chaieb K, Karray-Bouraoui N, Trabelsi N, Boulaaba M, Abdelly C (2008) Phenolic composition of Cynara cardunculus L. organs, and their biological activities. C R Biol 331:372–379
- Guettaf S, Abidli N, Kariche S, Bellebcir L, Bouriche H (2016) Phytochemical screening and antioxidant activity of aqueous extract of Genista Saharae (Coss. & Dur.). Pharm Lett 8:50–60
- Jeszka-Skowron M, Sentkowska A, Pyrzyńska K, De Peña MP (2016) Chlorogenic acids, caffeine content and antioxidant properties of green coffee extracts: influence of green coffee bean preparation. Eur Food Res Technol 242:1403–1409
- Jimoh FO, Adedapo AA, Afolayan AJ (2010) Comparison of the nutritional value and biological activities of the acetone, methanol and water extracts of the leaves of Solanum nigrum and Leonotis leonorus. Food Chem Toxicol 48:964–971
- Kalemba D, Kunicka A (2003) Antibacterial and antifungal properties of essential oils. Curr Med Chem 10:813–829
- Karamac M, Kosicska A, Pegg RB (2005) Comparison of radical-scavenging activities for selected phenolic acids. Pol J Food Nutr Sci 55:165–170
- Kelly EH, Anthony RT, Dennis JB (2002) Flavonoid antioxidants: chemistry, metabolism and structure-activity relationships. J Nutr Biochem 13:572–584
- Laguerre M, López-Giraldo LJ, Lecomte J, Pina M, Villeneuve P (2007) Outils d’évaluation in vitro de la capacité antioxydante. OCL 14:278–292
- Martins HFP, Leal JP, Fernandez MT (2004) Toward the prediction of the activity of antioxidants: experimental and theoretical study of the gas-phase acidities of flavonoids. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 15:848–861
- Miliauskas G, Venskutoni PR, Van Beek TA (2004) Screening of radical scavenging activity of some medicinal and aromatic plant extracts. Food Chem 85:231–237
- Oyaizu M (1986) Study on products of browing reactions: Antioxidative activities of browing reaction prepared from glucosamine. JPN J Nutr 44:307–315
- Panusa A, Zuorro A, Lavecchia R, Marrosu G, Petrucci R (2013) Recovery of natural antioxidants from spent coffee grounds. J Agric Food Chem 61:4162–4168
- Papuc C, Goran GV, Predescu CN, Nicorescu V, Stefan G (2017) Plant polyphenols as antioxidant and antibacterial agents for shelf-life extension of meat and meat products: classification, structures, sources, and action mechanisms. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf 16:1243–1268
- Re R, Pellegrini N, Proteggente A, Pannala A, Yang M, Rice-Evans C (1999) Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radic Bio Med 26:1231–1237
- Robards K, Prenzler PD, Tucker G, Swatsitang P, Glover W (1999) Phenolic compounds and their role in oxidative processes in fruits. Food Chem 66:401–436
- Sandhar HK, Kumar B, Prasher S, Tiwari P, Salhan M, Sharma PA (2011) Review of phytochemistry and pharmacology of flavonoids. IPS 1:25–41
- Siddhuraju P, Becker K (2007) The antioxidant and free radical scavenging activities of processed cowpea (Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp.) seed extracts. Food Chem 101:10–19
- Slobodníková L, Fialová S, Rendeková K, Kováč J, Mučaji P (2016) Antibiofilm activity of plant polyphenols. Molecules 21:1717
- Stagos D, Portesis N, Spanou C, Mossialos D, Aligiannis N, Chaita E, Panagoulis C, Reri E, Skaltsounis L, Tsatsakis AM, Kouretas D (2012) Correlation of total polyphenolic content with antioxidant and antibacterial activity of 24 extracts from Greek domestic Lamiaceae species. Food Chem Toxicol 50:4115–4124
- Stojković D, Petrović J, Soković M, Glamočlija J, Kukić-Marković J, Petrović S (2013) In situ antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of naturally occurring caffeic acid, p-coumaric acid and rutin, using food systems. J Sci Food Agric 93:3205–3208
- Szydlowska-Czerniaka A, Dianoczki C, Recseg K, Karlovits G, Szlyk E (2008) Determination of antioxidant capacities of vegetable oils by ferric-ion spectrophotometric methods. Talanta 76:899–905
- Tabart J, Kevers C, Pincemail J, Defraigne J, Dommes J (2009) Comparative antioxidant capacities of phenolic compounds measured by various tests. Food Chem 113:1226–1233
- Treml J, Šmejkal K (2016) Flavonoids as potent scavengers of hydroxyl radicals. Compr Rev Food Sci Food 15:720–738
- Upson TM, Grayer RJ, Greenham JR, Williams CA, Al-Ghamdi F, Chen F (2000) Leaf flavonoids as systematic characters in the Genera lavandula and Sabaudia. Biochem Syst Ecol 28:991–1007
- Vermerris W, Nicholson R (2006) Isolation and identification of phenolic compounds biochemistry. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 35–62–151–191
- Xiao ZT, Zhu Q, Zhang HY (2014) Identifying antibacterial targets of flavonoids by comparative genomics and molecular modeling. OJGEN 3:1
- Yazdanparast R, Ardestani A (2007) In vitro antioxidant and free radical scavenging activity of Cyperus rotundus. J MED food 10:667–674
- Zhang L, Khoo C, Koyyalamudi SR, de Pedro N, Reddy N (2017) Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and anticancer activities of ethanol soluble organics from water extracts of selected medicinal herbs and their relation with flavonoid and phenolic contents. Pharmacologia 8:59–72
Author Information
Laboratoire Antibiotiques Antifongiques: physico-chimie, synthèse et activité biologique, Département de Biologie, Faculté SNV-STU, Université Aboubekr Belkaïd-Tlemcen, Imama, Algeria